A Culinary Journey Around The World: Exploring The Food Map
A Culinary Journey Around the World: Exploring the Food Map
Related Articles: A Culinary Journey Around the World: Exploring the Food Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Culinary Journey Around the World: Exploring the Food Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Culinary Journey Around the World: Exploring the Food Map
The world is a vibrant tapestry of cultures, each with its unique traditions and expressions, and food is a central element in this tapestry. A "food map" serves as a visual and conceptual guide to understanding the diverse culinary landscapes across the globe. It reveals not just the ingredients and dishes that define each region, but also the historical, geographical, and cultural factors that have shaped these culinary traditions.
Understanding the Food Map: A Global Culinary Tapestry
The food map is more than just a collection of recipes; it’s a reflection of human ingenuity and adaptation. It reveals how people have utilized available resources, embraced cultural influences, and developed culinary practices that are deeply intertwined with their environment and way of life.
Factors Shaping the Food Map:
- Geography and Climate: The natural landscape plays a pivotal role in shaping culinary traditions. Coastal regions often feature seafood-heavy cuisines, while mountainous areas may rely on hearty, protein-rich dishes. Tropical climates boast vibrant fruits and vegetables, while arid regions utilize grains and spices to create flavorful meals.
- History and Trade: Historical events, migration patterns, and trade routes have significantly impacted the food map. The Silk Road, for instance, facilitated the exchange of spices and culinary techniques between Asia and Europe, influencing cuisines across vast distances. Colonialism also left its mark, introducing new ingredients and cooking methods to various parts of the world.
- Culture and Religion: Cultural beliefs and religious practices often dictate dietary choices. For example, Hinduism emphasizes vegetarianism, while Islamic traditions prohibit the consumption of pork. These cultural and religious influences contribute to the diverse array of cuisines found across the globe.
- Modernization and Globalization: The modern world has accelerated the exchange of culinary ideas and ingredients. Globalization has led to the fusion of cuisines, resulting in innovative dishes that blend traditional flavors with modern techniques.
Navigating the Food Map: A Culinary Exploration
Exploring the food map is an enriching experience that deepens our understanding of the world’s diverse cultures and their culinary expressions. Here’s a glimpse into some of the key regions and their culinary highlights:
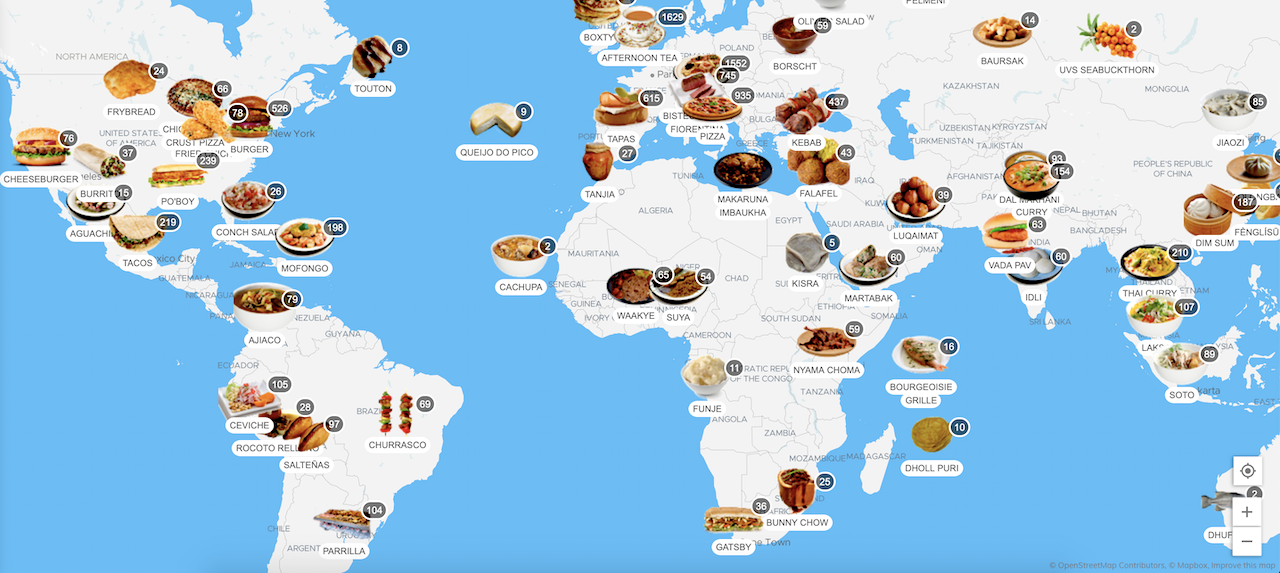
1. Asia:
- East Asia: Known for its emphasis on fresh ingredients, delicate flavors, and artful presentation. Japan’s sushi, China’s stir-fries, and Korea’s kimchi are iconic examples of this region’s culinary prowess.
- Southeast Asia: Characterized by fragrant spices, bold flavors, and the use of coconut milk, rice, and noodles. Thailand’s curries, Vietnam’s pho, and Indonesia’s satay are just a few examples of the diverse cuisine found in this region.
- South Asia: Renowned for its vibrant spices, vegetarian dishes, and the use of rice and lentils. India’s curries, Pakistan’s biryani, and Sri Lanka’s kottu roti are examples of this region’s rich culinary heritage.
2. Europe:
- Mediterranean: Known for its emphasis on fresh, seasonal ingredients, olive oil, and herbs. Italy’s pasta dishes, Greece’s moussaka, and Spain’s paella are iconic examples of this region’s culinary heritage.
- Northern Europe: Characterized by hearty, comfort food, often featuring potatoes, grains, and meat. Germany’s schnitzel, Sweden’s meatballs, and Denmark’s smørrebrød are examples of this region’s cuisine.
- Central Europe: Known for its rich, savory dishes, often featuring meat, dumplings, and sauerkraut. Austria’s Wiener Schnitzel, Hungary’s goulash, and Poland’s pierogi are examples of this region’s culinary traditions.
3. The Americas:
- North America: A melting pot of culinary influences, featuring dishes from various immigrant communities. The United States is known for its burgers, pizzas, and barbecue, while Canada boasts its poutine and maple syrup.
- Latin America: Characterized by its use of corn, beans, chilies, and spices. Mexico’s tacos, Peru’s ceviche, and Brazil’s feijoada are examples of this region’s diverse culinary landscape.
- South America: Known for its vibrant flavors, often featuring fresh seafood, vegetables, and spices. Argentina’s asado, Chile’s empanadas, and Colombia’s arepas are examples of this region’s culinary traditions.
4. Africa:
- North Africa: Influenced by Arab and Mediterranean cuisines, featuring spices, couscous, and tagines. Morocco’s tagine, Tunisia’s couscous, and Egypt’s ful medames are examples of this region’s culinary heritage.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Known for its diverse cuisines, often featuring grains, legumes, and meat. Ethiopia’s injera, Senegal’s thieboudienne, and South Africa’s boerewors are examples of this region’s culinary traditions.
The Importance of the Food Map
The food map is a powerful tool for understanding the world’s diverse cultures and their culinary expressions. It helps us:
- Appreciate Cultural Diversity: By exploring the food map, we gain insight into the traditions, beliefs, and values that shape each region’s culinary heritage.
- Promote Culinary Exploration: The food map encourages us to step outside our comfort zones and try new flavors and cuisines. It opens our minds to new culinary experiences and expands our palates.
- Foster Global Understanding: Understanding the food map helps us bridge cultural divides and build connections with people from different backgrounds. It promotes empathy and respect for diverse culinary traditions.
- Support Sustainable Food Systems: The food map highlights the importance of local ingredients and traditional cooking methods, promoting sustainable food practices that are in harmony with the environment.
FAQs about the Food Map:
Q: What is the best way to learn about the food map?
A: There are numerous ways to explore the food map:
- Travel: Experiencing different cultures firsthand is the most immersive way to learn about their culinary traditions.
- Cookbooks and Recipes: Explore cookbooks and online resources to discover recipes and culinary techniques from around the world.
- Food Festivals and Events: Attend food festivals and events to sample cuisines from various regions and learn about their history and traditions.
- Documentaries and TV Shows: Watch documentaries and TV shows that explore culinary traditions from different parts of the world.
Q: How can I use the food map to plan my meals?
A: The food map can inspire you to create meals that reflect different culinary traditions. You can:
- Choose ingredients from a specific region: Select ingredients that are characteristic of a particular region to create a meal that reflects its culinary heritage.
- Experiment with flavors and techniques: Explore different flavor profiles and cooking techniques to create dishes that are both familiar and unique.
- Learn about the history and culture behind the food: Research the history and cultural significance of the dishes you’re preparing to gain a deeper appreciation for their origins.
Q: Is there a specific way to organize the food map?
A: The food map can be organized in various ways, depending on the focus. Some common approaches include:
- Geographical Organization: Mapping cuisines by region or continent.
- Ingredient-Based Organization: Grouping cuisines based on common ingredients or flavor profiles.
- Culinary Technique-Based Organization: Categorizing cuisines based on cooking methods or techniques.
Tips for Exploring the Food Map:
- Be Open to New Experiences: Don’t be afraid to step outside your comfort zone and try new flavors and cuisines.
- Respect Cultural Traditions: Learn about the history and cultural significance of the dishes you’re trying to appreciate their origins.
- Support Local Cuisine: Patronize local restaurants and food vendors to experience authentic cuisines and support local businesses.
- Embrace Fusion Cuisine: Experiment with fusion cuisine, which blends elements from different culinary traditions to create unique and innovative dishes.
Conclusion:
The food map is a vibrant and ever-evolving representation of the world’s culinary diversity. It invites us to embark on a journey of discovery, exploration, and appreciation of the rich tapestry of flavors and traditions that define our planet. By understanding the food map, we gain a deeper understanding of different cultures, foster global connections, and promote sustainable food practices. Whether we’re traveling to distant lands or exploring new flavors in our own kitchens, the food map serves as a guide to the world’s culinary wonders.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Culinary Journey Around the World: Exploring the Food Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply