Mapping The Tumultuous Years: A Geographical Exploration Of Weimar Germany
Mapping the Tumultuous Years: A Geographical Exploration of Weimar Germany
Related Articles: Mapping the Tumultuous Years: A Geographical Exploration of Weimar Germany
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Tumultuous Years: A Geographical Exploration of Weimar Germany. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Tumultuous Years: A Geographical Exploration of Weimar Germany
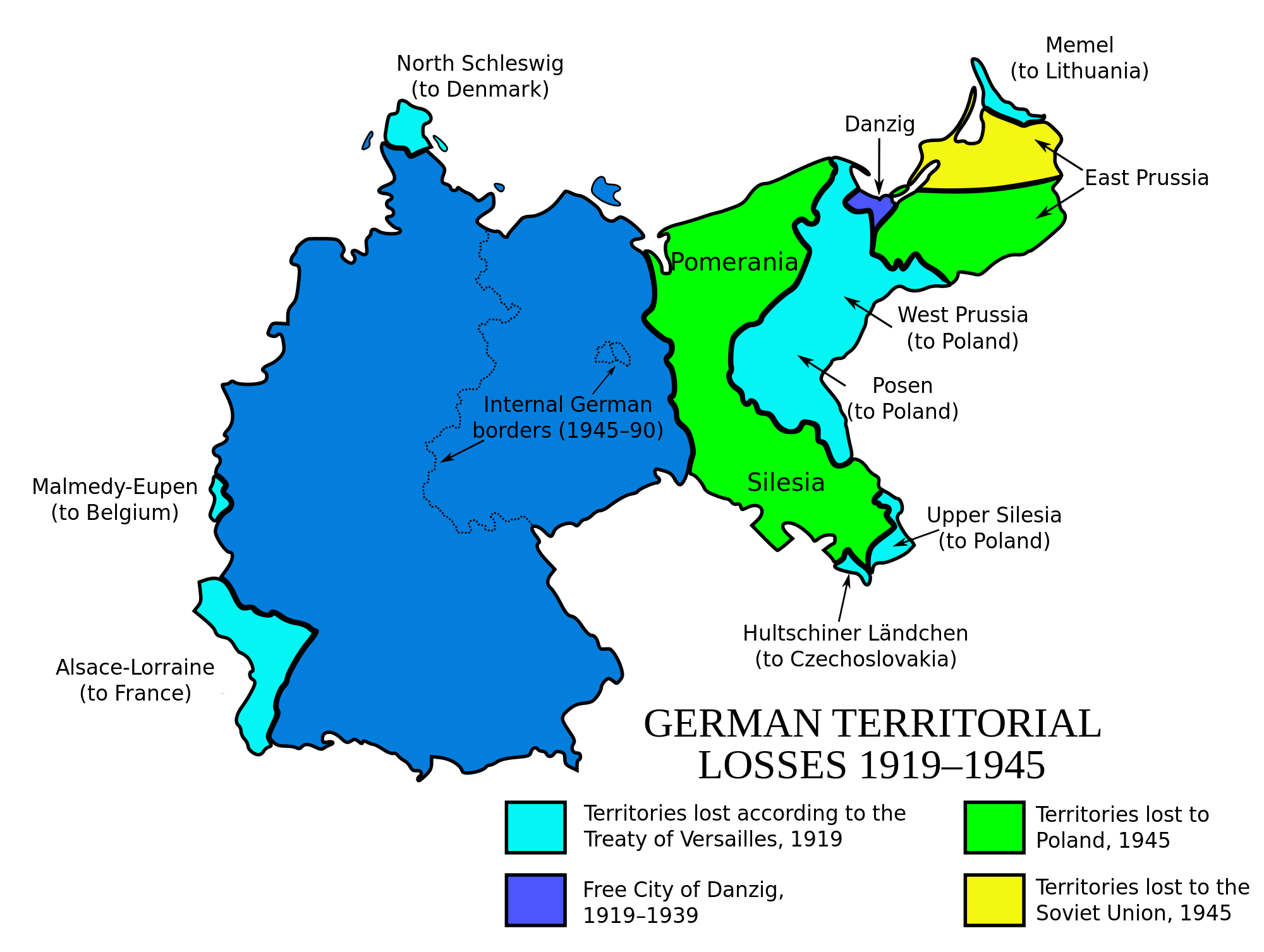
The Weimar Republic, a period in German history spanning from 1918 to 1933, stands as a pivotal chapter marked by political, economic, and social upheaval. Understanding the geographical context of Weimar Germany is crucial for comprehending the complexities of this era. Examining the map of Weimar Germany reveals not only the physical boundaries of the nation but also the intricate web of political, economic, and social forces that shaped its destiny.
A Nation Divided: The Territorial Landscape of Weimar Germany
The Weimar Republic inherited a fragmented territory from the defeated German Empire of World War I. The Treaty of Versailles, imposed by the victorious Allied powers, significantly altered Germany’s borders. The map of Weimar Germany showcases a nation stripped of its overseas colonies, vast swathes of territory in the east ceded to Poland and Czechoslovakia, and the strategically vital Saarland region placed under French administration for fifteen years.
The Rhineland: A Zone of Occupation and Political Tension
The Rhineland, a region bordering France and Belgium, was subjected to Allied occupation following World War I. This region served as a buffer zone aimed at preventing Germany from launching another offensive against its western neighbors. The presence of Allied troops in the Rhineland fueled resentment among German nationalists and contributed to the rise of extremist political movements.
Industrial Hubs and Economic Disparities
Weimar Germany boasted a robust industrial base, with major manufacturing centers concentrated in the Ruhr Valley, Saxony, and Silesia. These regions, characterized by heavy industries like coal mining, steel production, and chemical manufacturing, were crucial to the German economy. However, the economic prosperity of these industrial centers was starkly contrasted by the rural poverty prevalent in eastern Germany, particularly in agricultural areas.
The "Lost Territories": A Source of Nationalistic Sentiment
The loss of territories in the east, particularly the provinces of East Prussia and Upper Silesia, deeply impacted German national identity. These regions, historically considered integral parts of Germany, were now inhabited by significant Polish populations. The "lost territories" became a rallying cry for nationalist movements, who exploited the sense of grievance and territorial injustice to gain political traction.
Political Fragmentation and the Rise of Extremism
The map of Weimar Germany reflects the deep political divisions that characterized the republic. The political landscape was fragmented, with numerous political parties vying for power. The rise of extremist ideologies, particularly Nazism, found fertile ground in the economic and social turmoil that gripped the nation. The Nazi Party, initially a fringe movement, gained popularity by exploiting the widespread discontent and fear among the German population.
The Importance of Understanding the Weimar Germany Map
The map of Weimar Germany serves as a visual representation of the nation’s geopolitical realities and the internal tensions that ultimately led to its downfall. By studying the map, one can gain a deeper understanding of:
- The territorial consequences of the Treaty of Versailles: The map highlights the significant territorial losses and the impact on German national identity.
- The economic disparities between industrial centers and rural areas: The map reveals the uneven distribution of wealth and the social tensions that resulted from it.
- The rise of extremism: The map provides context for the emergence of nationalist and extremist movements, particularly the Nazi Party.
- The geopolitical pressures that shaped the Weimar Republic: The map underscores the international context in which the republic operated and the challenges it faced.
FAQs about the Weimar Germany Map
Q: What were the major territorial losses of Germany under the Treaty of Versailles?
A: Germany lost its overseas colonies, Alsace-Lorraine to France, parts of Upper Silesia to Poland, and the Memel Territory to Lithuania. The Saarland region was placed under French administration for fifteen years.
Q: What was the significance of the Rhineland occupation?
A: The Allied occupation of the Rhineland fueled resentment among German nationalists and contributed to the rise of extremist political movements. It also highlighted the lingering tensions between Germany and its western neighbors.
Q: How did the map of Weimar Germany reflect the economic disparities of the era?
A: The map demonstrates the concentration of industrial wealth in the Ruhr Valley, Saxony, and Silesia, while highlighting the economic hardship faced by rural areas in eastern Germany.
Q: What role did the "lost territories" play in the rise of nationalism?
A: The loss of territories in the east, particularly East Prussia and Upper Silesia, became a rallying cry for nationalist movements, who exploited the sense of grievance and territorial injustice to gain political traction.
Q: How did the political fragmentation of Weimar Germany contribute to its demise?
A: The lack of a strong, stable political system allowed extremist ideologies, particularly Nazism, to gain a foothold and eventually seize power.
Tips for Studying the Weimar Germany Map
- Identify the key geographical features: Focus on the borders, major cities, industrial centers, and regions of economic hardship.
- Consider the historical context: Analyze the map in relation to the Treaty of Versailles, the economic crisis, and the rise of extremism.
- Connect the map to primary sources: Use historical documents, photographs, and eyewitness accounts to gain a deeper understanding of the lived experiences of people in Weimar Germany.
- Compare the map to contemporary maps: Examine how the map of Weimar Germany differs from the map of modern-day Germany.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Turbulence and Transition
The map of Weimar Germany serves as a powerful reminder of the turbulent and transformative period in German history. It reveals a nation grappling with the aftermath of defeat, economic hardship, and political instability. Understanding the geographical context of Weimar Germany is crucial for comprehending the complexities of this era and its enduring legacy. The map not only provides a visual representation of the nation’s territorial boundaries but also sheds light on the social, economic, and political forces that shaped its destiny. The lessons learned from Weimar Germany continue to resonate in the contemporary world, reminding us of the fragility of democracy and the importance of addressing social and economic inequalities.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Tumultuous Years: A Geographical Exploration of Weimar Germany. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply