Navigating California’s Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Power Plant Locations
Navigating California’s Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Power Plant Locations
Related Articles: Navigating California’s Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Power Plant Locations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating California’s Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Power Plant Locations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating California’s Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Power Plant Locations

California, a state renowned for its environmental consciousness and commitment to renewable energy, also boasts a history of nuclear power generation. Understanding the locations of these power plants is crucial for comprehending the state’s energy landscape and its evolving relationship with nuclear technology. This article delves into the geographical distribution of nuclear power plants in California, exploring their historical context, operational status, and the ongoing discourse surrounding their future.
Mapping California’s Nuclear Past and Present
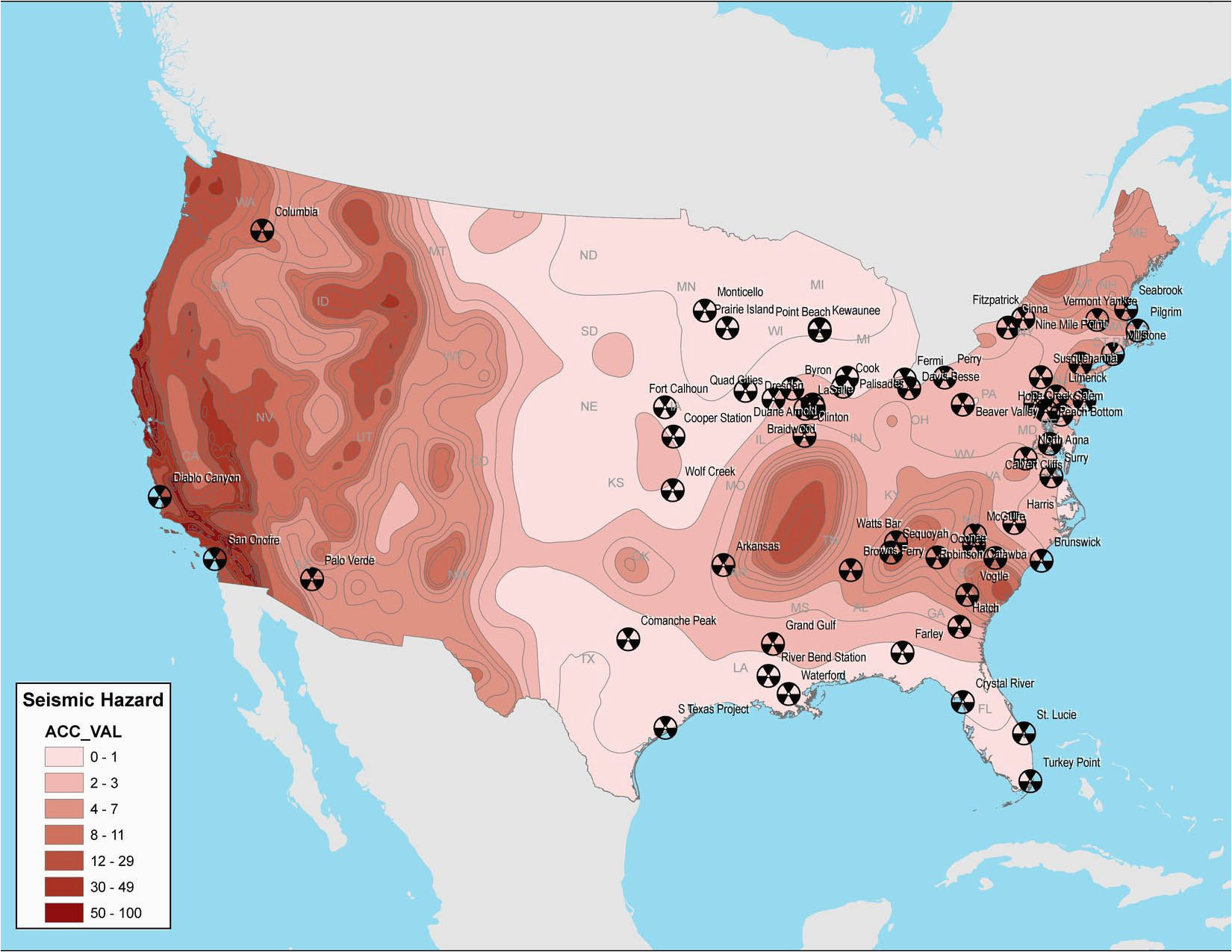
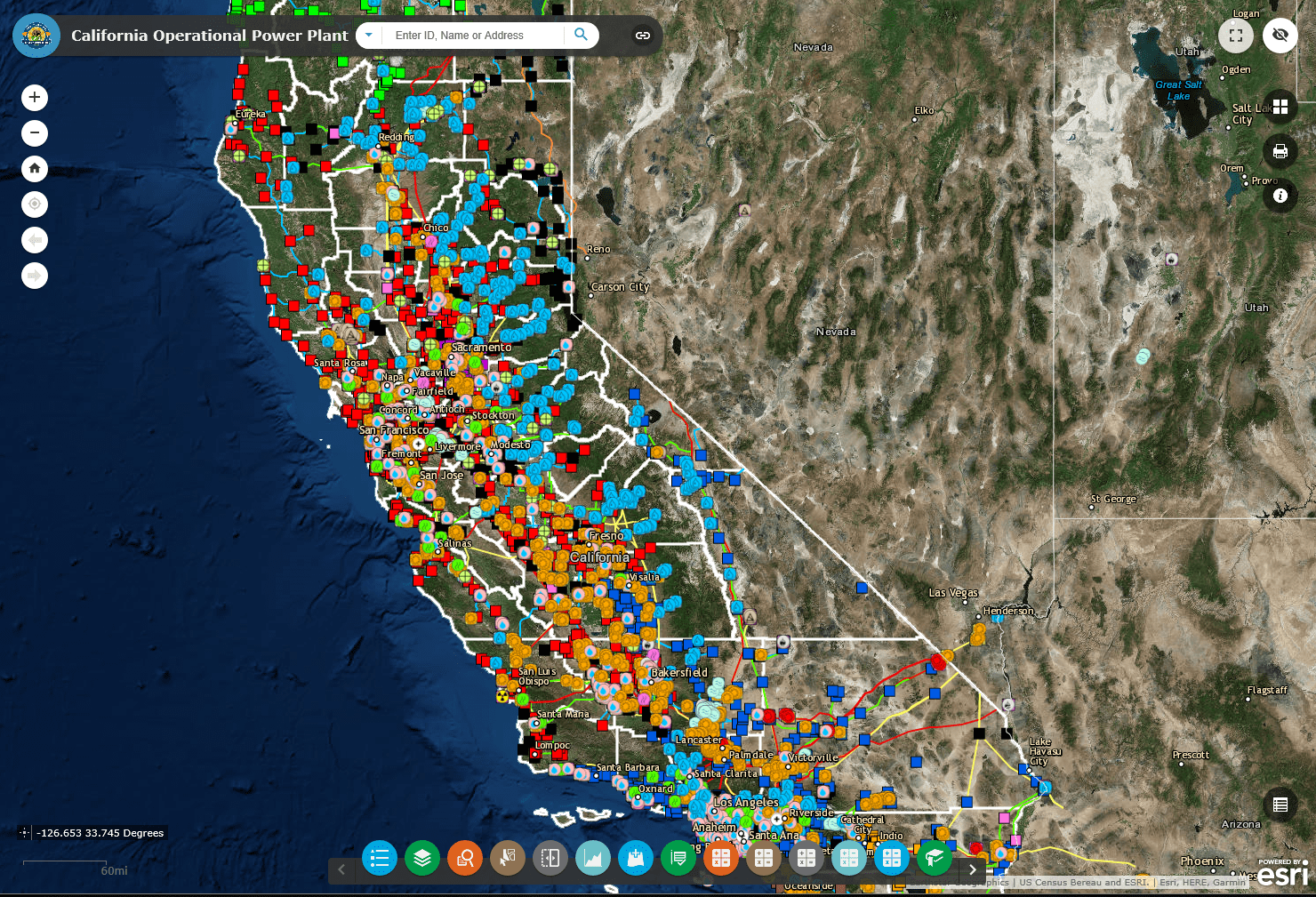
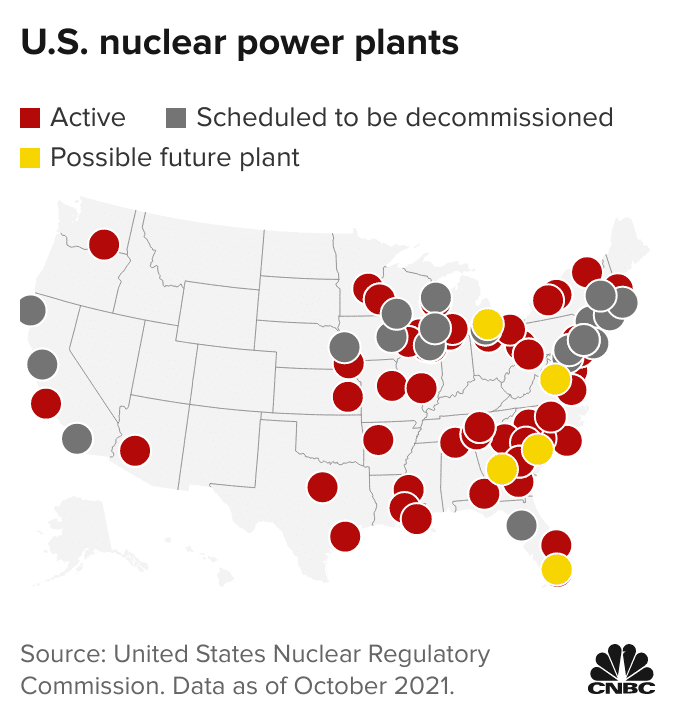
The map of nuclear power plants in California reveals a distribution primarily concentrated along the coast, reflecting the need for proximity to cooling water sources and access to major population centers.
-
Diablo Canyon Power Plant: Located in San Luis Obispo County, Diablo Canyon is California’s sole remaining operational nuclear power plant. It features two pressurized water reactors, generating approximately 2,200 megawatts of electricity. The plant’s future remains uncertain, with a scheduled closure in 2025, subject to potential legislative intervention.
-
San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station: Situated in San Clemente, San Onofre was once California’s largest nuclear power plant, featuring three pressurized water reactors. However, it permanently shut down in 2013 due to concerns about the aging steam generators and ongoing maintenance costs.
-
Humboldt Bay Power Plant: Situated in Humboldt County, this plant was California’s first commercial nuclear power plant, operating from 1963 to 1976. It was a boiling water reactor with a capacity of 65 megawatts. After experiencing operational challenges, it was permanently decommissioned.
The Role of Nuclear Power in California’s Energy Mix
Nuclear power has played a significant role in California’s energy mix, providing a reliable and carbon-free source of electricity for decades. However, its future remains a subject of debate, driven by factors such as:
- Safety Concerns: The 2011 Fukushima disaster in Japan heightened public awareness of the potential risks associated with nuclear power, prompting renewed safety concerns.
- Waste Management: The long-term storage and disposal of nuclear waste continue to pose significant challenges.
- Economics: The high upfront costs of constructing nuclear power plants, combined with regulatory complexities, have made it less economically attractive compared to other energy sources.
- Renewable Energy Expansion: California’s ambitious renewable energy goals, particularly in solar and wind power, have led to a shift in focus away from nuclear power.
The Future of Nuclear Power in California
The future of nuclear power in California is uncertain, with various stakeholders advocating for different approaches. Some argue for continued operation of existing plants, emphasizing their role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Others advocate for closure, citing safety concerns and the availability of alternative renewable energy sources.
The debate surrounding the future of nuclear power in California is complex, involving considerations of energy security, environmental sustainability, and economic feasibility. It requires careful analysis, public engagement, and thoughtful policy decisions to ensure a balanced approach that meets the state’s energy needs while addressing the multifaceted concerns surrounding nuclear technology.
FAQs on Nuclear Power Plants in California
1. What is the current status of nuclear power plants in California?
Currently, only Diablo Canyon Power Plant remains operational. San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station was permanently shut down in 2013, and Humboldt Bay Power Plant was decommissioned in 1976.
2. Why was San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station closed?
The closure of San Onofre was primarily due to concerns about the aging steam generators and ongoing maintenance costs. The plant’s operators faced significant financial challenges, leading to the decision to permanently shut it down.
3. What are the potential benefits of nuclear power?
Nuclear power is a carbon-free source of electricity, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. It also provides a reliable and consistent energy source, particularly important for meeting baseload demand.
4. What are the potential risks associated with nuclear power?
Nuclear power plants pose risks of accidents, such as the Fukushima disaster, which can have severe environmental and health consequences. The long-term storage and disposal of nuclear waste also present significant challenges.
5. What is the future of Diablo Canyon Power Plant?
Diablo Canyon is scheduled to close in 2025. However, there are ongoing efforts to extend its operational lifespan, driven by concerns about energy security and the need to maintain a carbon-free energy source.
Tips for Understanding Nuclear Power in California
- Engage with credible sources: Consult reputable organizations like the California Energy Commission, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, and environmental advocacy groups for accurate information.
- Explore different perspectives: Consider the arguments presented by both proponents and opponents of nuclear power, understanding the complexities of the issue.
- Stay informed about policy developments: Follow legislative debates and regulatory changes related to nuclear power in California.
- Participate in public discussions: Attend community forums and engage in dialogue about the future of nuclear power in your region.
Conclusion
The map of nuclear power plants in California provides a visual representation of the state’s historical reliance on nuclear energy. While the future of this technology remains uncertain, its legacy continues to influence California’s energy landscape. Understanding the location, history, and ongoing debate surrounding these power plants is crucial for navigating the complex and evolving landscape of energy generation in the state. As California strives to achieve its ambitious renewable energy goals, the role of nuclear power will continue to be a subject of ongoing discussion and critical assessment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating California’s Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Power Plant Locations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply