Navigating The City That Never Sleeps: A Comprehensive Guide To The E Train In New York City
Navigating the City That Never Sleeps: A Comprehensive Guide to the E Train in New York City
Related Articles: Navigating the City That Never Sleeps: A Comprehensive Guide to the E Train in New York City
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the City That Never Sleeps: A Comprehensive Guide to the E Train in New York City. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the City That Never Sleeps: A Comprehensive Guide to the E Train in New York City
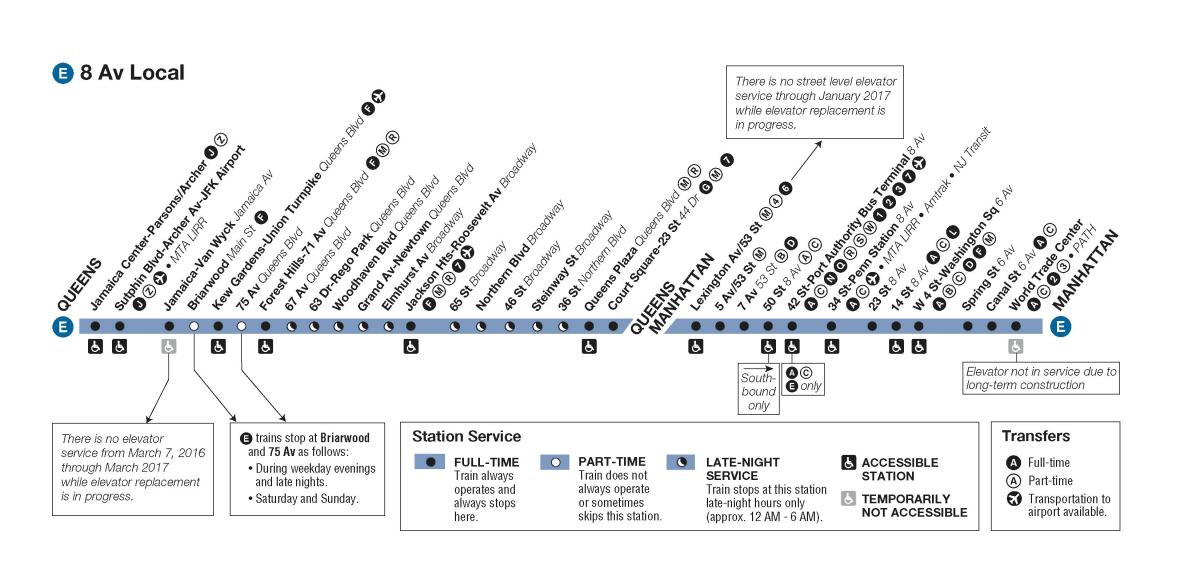
New York City, a bustling metropolis renowned for its vibrant culture, diverse neighborhoods, and iconic landmarks, is a city best explored by its extensive and efficient subway system. The E train, a vital artery in this intricate network, traverses the city’s landscape, connecting riders to a multitude of destinations. This guide delves into the intricacies of the E train, providing a comprehensive understanding of its route, stops, connections, and its significance in the city’s transportation infrastructure.
Understanding the E Train’s Route and Stops
The E train, part of the New York City Subway’s IND Eighth Avenue Line, operates along a distinctive route that spans across Manhattan and Queens. It begins its journey in the heart of Manhattan at World Trade Center station, a hub of international commerce and a symbol of resilience. From there, it travels north, serving several key stops along the way:
- World Trade Center: This station, located in the Financial District, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, C, and R trains, providing easy access to various parts of Manhattan and Brooklyn.
- Fulton Street: This station, situated in the heart of Lower Manhattan, provides connections to the 2, 3, 4, 5, A, C, J, and Z trains, offering extensive connections to various parts of the city.
- Chambers Street: This station, located in the Tribeca neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to the West Village, Greenwich Village, and Midtown.
- Canal Street: This station, located in the Chinatown and Little Italy neighborhoods, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, 6, J, M, N, Q, R, and W trains, providing access to various parts of Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Queens.
- Spring Street: This station, located in the SoHo neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to the Lower East Side and the East Village.
- Houston Street: This station, located in the NoHo neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to the Lower East Side and the East Village.
- Bleecker Street: This station, located in the Greenwich Village neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to the West Village and Washington Square Park.
- 8th Street-New York University: This station, located in the Greenwich Village neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to Washington Square Park and the East Village.
- 14th Street: This station, located in the Union Square neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, L, N, Q, R, 4, 5, and 6 trains, providing access to various parts of Manhattan and Brooklyn.
- 23rd Street: This station, located in the Flatiron District, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to Chelsea and the Meatpacking District.
- 28th Street: This station, located in the Chelsea neighborhood, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, and A trains, providing access to the Meatpacking District and the West Village.
- 34th Street-Herald Square: This station, located in Midtown, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, 7, A, C, E, B, D, F, M, N, Q, R, and W trains, providing access to various parts of Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Queens.
- 42nd Street-Port Authority Bus Terminal: This station, located in Midtown, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, 7, A, C, E, N, Q, R, S, and W trains, providing access to various parts of Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Queens.
- 50th Street: This station, located in Midtown, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, 7, and A trains, providing access to Rockefeller Center and Times Square.
- 59th Street-Columbus Circle: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
From 59th Street-Columbus Circle, the E train continues into Queens, serving the following stops:
- 72nd Street: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
- 86th Street: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
- 96th Street: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
- 103rd Street: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
- 110th Street: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
- 116th Street: This station, located in the Upper West Side, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Central Park and Lincoln Center.
- 125th Street: This station, located in Harlem, offers connections to the 1, 2, 3, A, B, C, D, and 1 train, providing access to Harlem and the Upper West Side.
- 138th Street-Grand Concourse: This station, located in the Bronx, offers connections to the 4, 5, and B, D trains, providing access to the Bronx and Manhattan.
The E train’s route provides convenient access to various neighborhoods, landmarks, and cultural institutions, including:
- Financial District: Home to Wall Street, the New York Stock Exchange, and the iconic Charging Bull statue.
- Chinatown and Little Italy: Vibrant neighborhoods with diverse culinary offerings and cultural attractions.
- SoHo and Tribeca: Trendy neighborhoods known for their art galleries, boutiques, and historic architecture.
- Greenwich Village: A bohemian neighborhood with a rich history, renowned for its music scene, bookstores, and Washington Square Park.
- Union Square: A bustling hub with a farmers market, shopping, and entertainment options.
- Midtown: Home to Times Square, Rockefeller Center, and numerous theaters.
- Upper West Side: A residential neighborhood with a strong cultural presence, featuring Central Park, Lincoln Center, and the American Museum of Natural History.
- Harlem: A historically significant neighborhood known for its music, culture, and vibrant community.
- The Bronx: Home to the New York Botanical Garden, the Bronx Zoo, and Yankee Stadium.
Importance and Benefits of the E Train
The E train plays a crucial role in the city’s transportation infrastructure, providing numerous benefits for commuters and visitors alike:
- Efficient Transportation: The E train offers a fast and efficient mode of transportation, connecting riders to various parts of Manhattan and Queens.
- Accessibility: The E train provides accessible transportation to numerous neighborhoods, landmarks, and cultural institutions, making it a valuable resource for residents and visitors.
- Connections: The E train offers numerous connections to other subway lines, providing easy access to various parts of the city.
- Cost-Effective: The E train is a cost-effective mode of transportation, offering affordable fares compared to other forms of transportation.
- Reliable Service: The E train operates on a regular schedule, providing reliable service for commuters and visitors.
- Reduced Congestion: The E train helps alleviate traffic congestion on city streets, providing a more efficient mode of transportation.
- Environmental Sustainability: The E train contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on personal vehicles, leading to lower emissions.
FAQs about the E Train
Q: What are the operating hours of the E train?
A: The E train operates 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. However, service may be reduced during late nights and early mornings.
Q: What is the frequency of E train service?
A: The frequency of E train service varies depending on the time of day and day of the week. During peak hours, trains run every 2-3 minutes. During off-peak hours, trains run every 4-6 minutes.
Q: How much does it cost to ride the E train?
A: The cost of riding the E train is $2.75 for a single ride. There are also various fare options available, including MetroCards, which offer discounted fares for multiple rides.
Q: What are the accessibility features of the E train?
A: The E train is accessible to individuals with disabilities. Most stations have elevators and ramps, and trains have designated areas for wheelchair users.
Q: What are the safety measures in place on the E train?
A: The E train is equipped with various safety measures, including surveillance cameras, emergency intercoms, and security personnel. Riders are encouraged to be aware of their surroundings and report any suspicious activity.
Tips for Riding the E Train
- Plan Your Trip: Utilize the MTA website or mobile app to plan your trip and check for any service disruptions or delays.
- Purchase a MetroCard: Purchase a MetroCard for discounted fares, especially if you plan to use the subway frequently.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Be aware of your surroundings and report any suspicious activity to authorities.
- Follow Posted Instructions: Follow all posted instructions and safety guidelines.
- Be Courteous to Other Riders: Be courteous to other riders and avoid blocking doorways or aisles.
- Keep Your Belongings Secure: Keep your belongings secure and avoid leaving valuables unattended.
- Be Prepared for Delays: Be prepared for potential delays, especially during peak hours or inclement weather.
Conclusion
The E train is an integral part of New York City’s transportation infrastructure, providing efficient, accessible, and reliable transportation for millions of commuters and visitors each year. Its extensive route connects numerous neighborhoods, landmarks, and cultural institutions, making it a vital resource for exploring the city’s diverse landscape. By understanding the E train’s route, stops, connections, and safety measures, riders can navigate the city with ease and enjoy all that New York City has to offer.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the City That Never Sleeps: A Comprehensive Guide to the E Train in New York City. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply