Navigating The Waters: Understanding FEMA Flood Maps In Louisiana
Navigating the Waters: Understanding FEMA Flood Maps in Louisiana
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding FEMA Flood Maps in Louisiana
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding FEMA Flood Maps in Louisiana. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters: Understanding FEMA Flood Maps in Louisiana
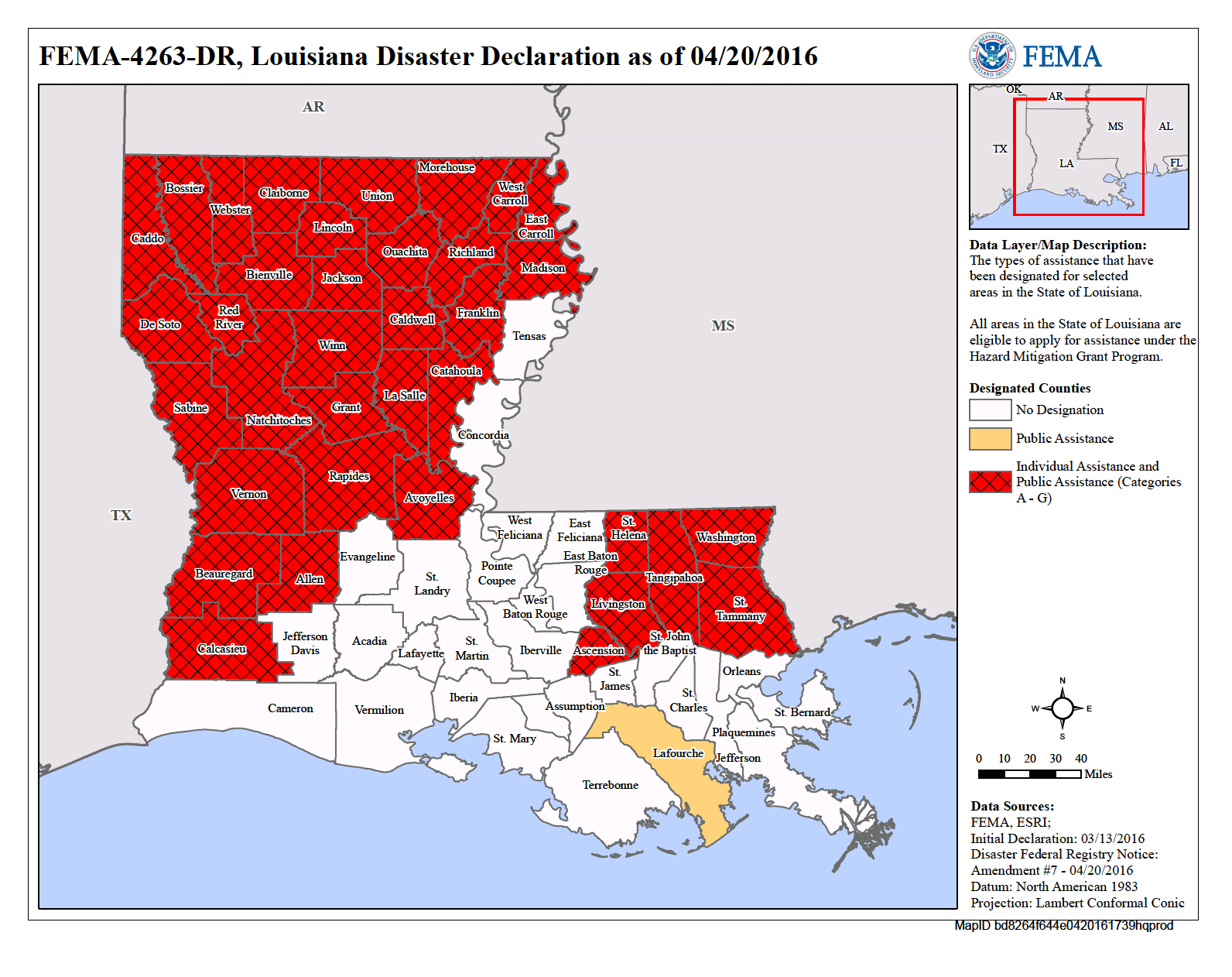
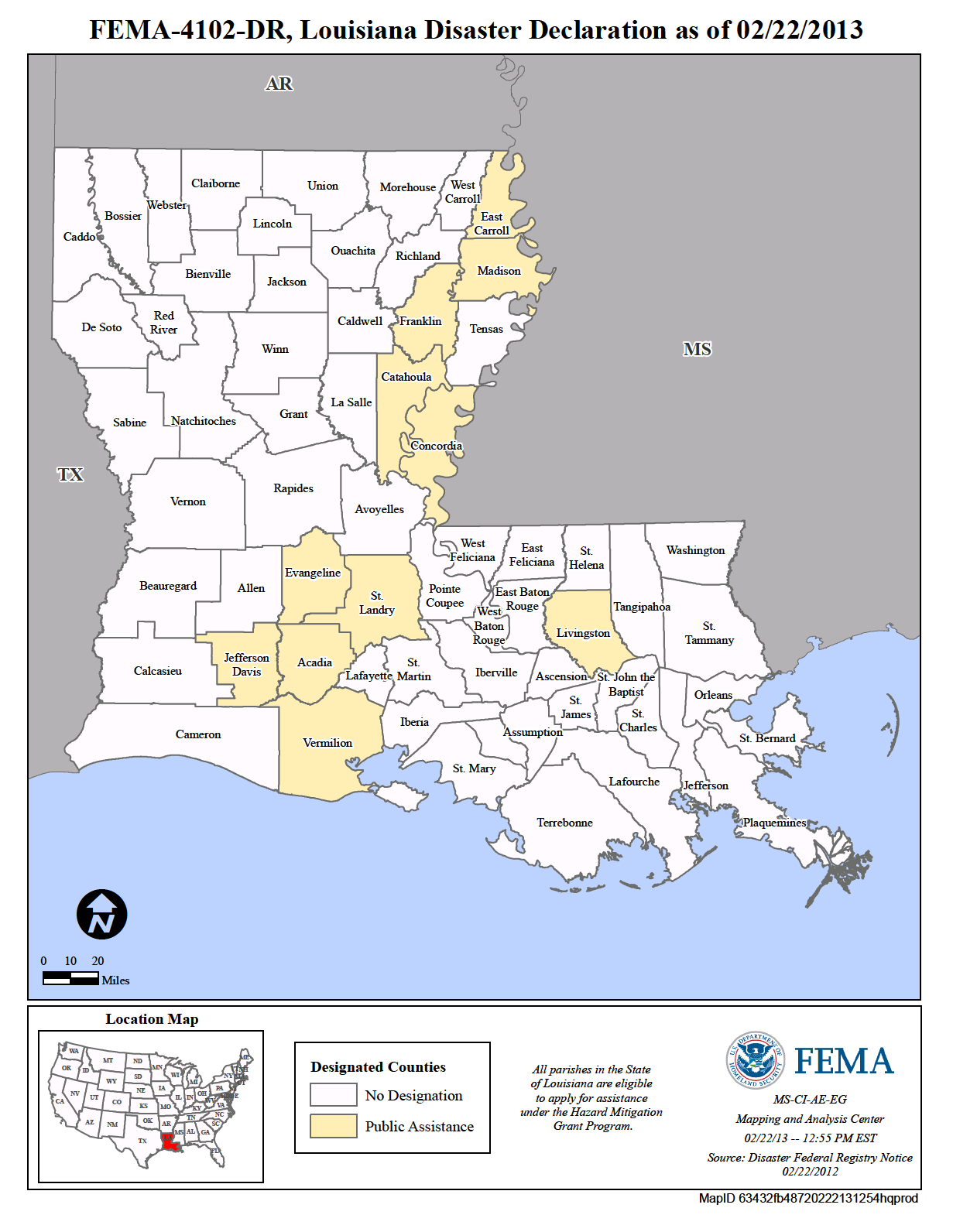
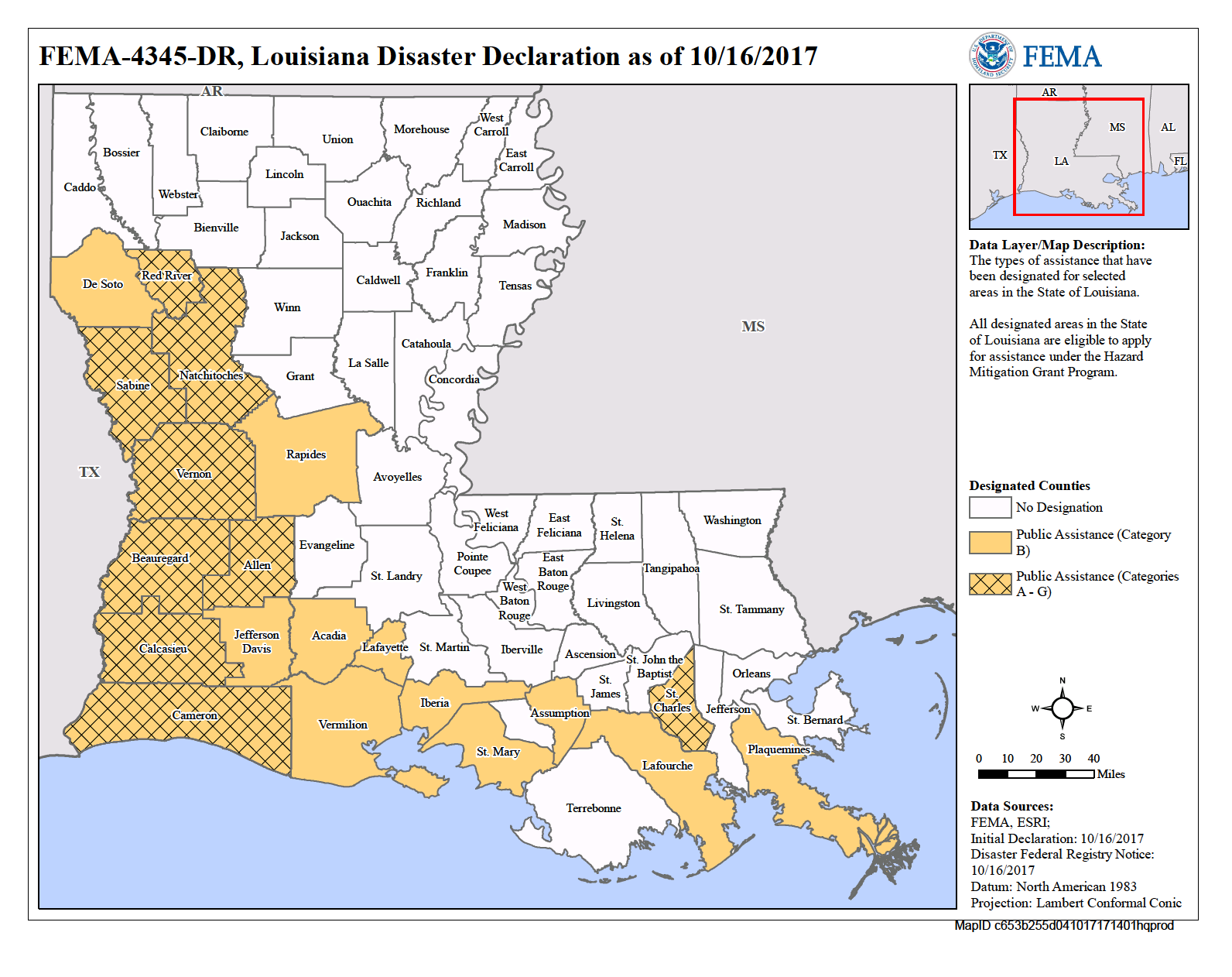
Louisiana, a state renowned for its picturesque waterways and coastal beauty, faces a constant and significant threat: flooding. This threat, amplified by rising sea levels, increasingly powerful storms, and the natural dynamics of the Mississippi River, necessitates comprehensive flood risk assessment and mitigation strategies. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), recognizing the importance of this task, has developed a crucial tool for understanding and mitigating flood risk: the Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM).
Understanding the FEMA Flood Map
The FEMA Flood Map, often referred to as the FIRM, serves as a visual representation of flood risk across the United States. This map identifies areas susceptible to flooding from various sources, including rivers, coastal waters, and storm surge. The map is divided into flood zones, each categorized by the likelihood of flooding and the depth of floodwaters.
Louisiana’s Unique Flood Risk Landscape
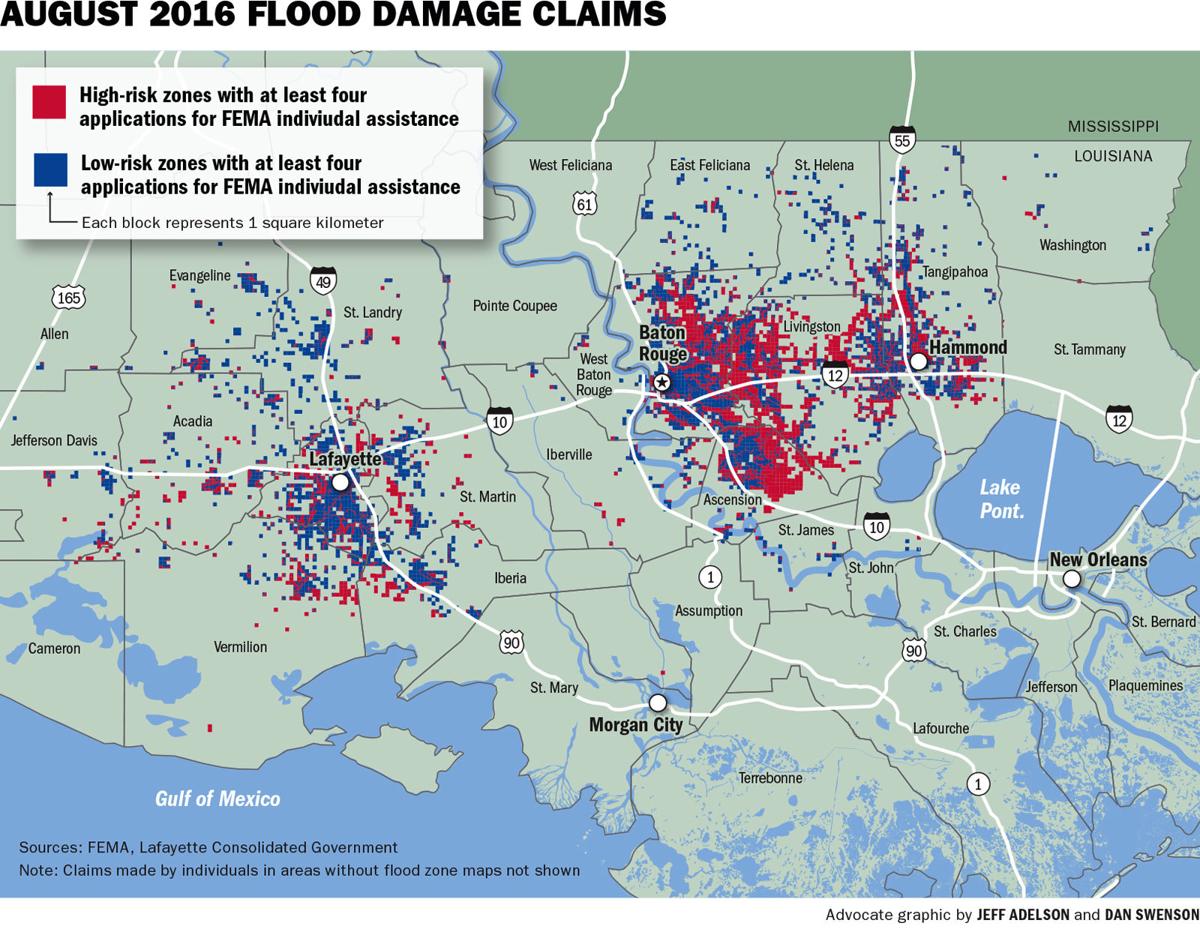
Louisiana’s geography, characterized by its extensive coastline, numerous rivers, and low-lying terrain, makes it particularly vulnerable to flooding. The state faces a multifaceted flood risk, encompassing:
- Coastal Flooding: The state’s vast coastline is exposed to the constant threat of storm surge, which can be exacerbated by hurricanes and tropical storms. Rising sea levels further amplify this risk.
- Riverine Flooding: The Mississippi River, along with its tributaries, plays a vital role in Louisiana’s ecosystem and economy. However, heavy rainfall and upstream flooding can lead to significant riverine flooding, impacting communities along its banks.
- Urban Flooding: Rapid urbanization and inadequate drainage infrastructure can exacerbate flooding in urban areas, particularly during heavy rainfall events.
The Importance of the FEMA Flood Map for Louisiana
The FEMA Flood Map holds paramount importance for Louisiana, serving as a critical tool for:
- Flood Risk Assessment: The map provides a comprehensive understanding of flood risk across the state, helping individuals, communities, and policymakers make informed decisions regarding flood mitigation and preparedness.
- Flood Insurance Requirements: The FIRM is used to determine flood insurance requirements for properties located in designated flood zones. This ensures that homeowners and businesses have access to financial protection in the event of a flood.
- Land Use Planning and Development: The map informs land use planning and development decisions, ensuring that new construction projects are located in areas less susceptible to flooding and minimizing potential risks.
- Emergency Response and Recovery: The map assists emergency responders in understanding potential flood impacts and allocating resources effectively during flood events.
Navigating the FEMA Flood Map: A Guide for Louisiana Residents
Understanding the information contained within the FEMA Flood Map is crucial for Louisiana residents. Here’s a breakdown of key elements:
-
Flood Zones: The map is divided into various flood zones, each representing a different level of flood risk. Some common zones include:
- Zone A: Areas with a 1% chance of flooding annually (the "100-year floodplain").
- Zone X: Areas with a less than 1% chance of flooding annually.
- Zone AE: Areas with a 1% chance of flooding annually and where flood depths are known.
- Zone AH: Areas with a 1% chance of flooding annually and where flood depths are known, but base flood elevations are not.
- Zone AO: Areas with a 1% chance of flooding annually, typically due to coastal flooding.
- Base Flood Elevation (BFE): The BFE represents the elevation to which floodwaters are expected to rise during a 100-year flood event. This information is crucial for determining building requirements in flood-prone areas.
- Floodway: The floodway is a designated area within a floodplain that must remain unobstructed to allow floodwaters to flow freely. Construction within the floodway is typically prohibited.
FEMA Flood Map: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I find my property’s flood zone on the FEMA Flood Map?
A: You can access the FEMA Flood Map online through the FEMA website (www.fema.gov) or through the Louisiana Office of Homeland Security and Emergency Preparedness (GOHSEP) website. Enter your address to locate your property on the map.
Q: What does it mean if my property is located in a flood zone?
A: If your property is located in a flood zone, you are required to purchase flood insurance if you have a federally backed mortgage. Additionally, you may need to meet specific building requirements to ensure your property is elevated or protected from flood damage.
Q: What are the benefits of purchasing flood insurance?
A: Flood insurance provides financial protection in the event of a flood, covering losses to your property and possessions. Without flood insurance, you may face significant financial hardship if your property is damaged by flooding.
Q: How do I obtain flood insurance?
A: Flood insurance can be purchased through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) or through private insurance companies. You can contact an insurance agent to obtain a quote and learn more about coverage options.
Q: Can I appeal my flood zone designation?
A: You can appeal your flood zone designation if you believe it is inaccurate or unfair. You can file an appeal with FEMA through the Letter of Map Amendment (LOMA) process.
Q: What are some tips for reducing flood risk on my property?
A: You can take several steps to reduce flood risk on your property, including:
- Elevating your home: If possible, elevate your home above the BFE to minimize flood damage.
- Installing flood vents: Flood vents allow floodwaters to enter your home’s crawl space, preventing hydrostatic pressure buildup that can cause damage.
- Creating a flood emergency plan: Develop a plan outlining how you will evacuate your home and protect your belongings in the event of a flood.
- Protecting your belongings: Store valuable items and electronics above the BFE to prevent damage.
Conclusion
The FEMA Flood Map serves as a vital tool for understanding and mitigating flood risk in Louisiana. By understanding the information contained within the map, residents and policymakers can make informed decisions to protect lives, property, and infrastructure from the threat of flooding. The map empowers individuals to take proactive steps to reduce their flood risk, fostering a safer and more resilient community for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding FEMA Flood Maps in Louisiana. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply