Navigating The World: A Comprehensive Guide To Creating Location Maps
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Location Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Location Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Location Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Location Maps

Location maps, often referred to as site plans or area maps, are visual representations of physical spaces. They serve as essential tools for various purposes, from guiding visitors through a building to illustrating the layout of a city or even the entire globe. This comprehensive guide delves into the creation of location maps, exploring their importance, benefits, and the diverse methods employed to craft them.
Understanding the Purpose and Importance of Location Maps
Location maps transcend mere visual representations; they function as powerful communication tools. Their primary objective is to provide clear and concise information about a specific location, enabling users to easily navigate and understand its layout. This clarity is crucial in various contexts:
1. Navigation and Orientation: Location maps provide a visual framework for navigating unfamiliar environments. Whether it’s a visitor exploring a museum or a resident seeking a specific store in a shopping mall, these maps offer a sense of direction and help users find their way.
2. Information Dissemination: Location maps serve as effective mediums for conveying important information about a location. They can highlight key features, points of interest, emergency exits, and other crucial details, ensuring that users are well-informed and prepared.
3. Planning and Development: Location maps play a vital role in planning and development projects. Architects, urban planners, and landscape designers utilize them to visualize and communicate their proposed designs, facilitating collaboration and decision-making.
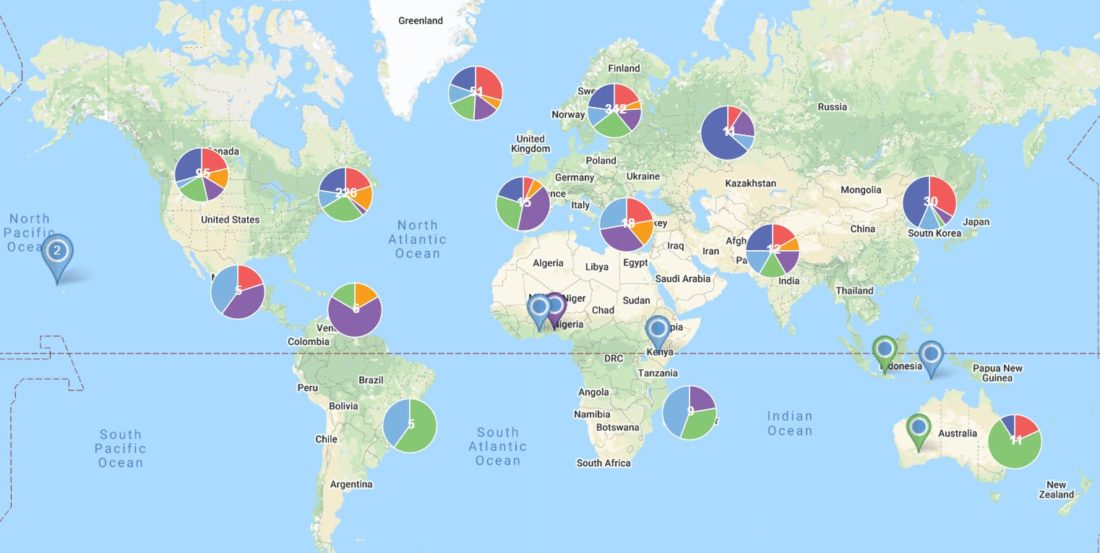
4. Data Visualization: Location maps are powerful tools for visualizing data related to specific locations. For example, they can depict population density, crime rates, or environmental factors, enabling analysis and informed decision-making.
5. Education and Research: Location maps are valuable resources for educational and research purposes. They provide visual representations of historical events, geographical features, or scientific data, facilitating learning and understanding.
Methods for Creating Location Maps
The creation of location maps involves a systematic approach that encompasses various methods and tools. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Data Collection and Preparation:
- Identifying the Location: The first step is to clearly define the location that will be represented on the map. This includes specifying the area’s boundaries, geographical coordinates, and any relevant landmarks.
-
Gathering Data: Data collection is crucial for creating an accurate and informative map. This involves gathering information on key features, points of interest, buildings, roads, and other relevant elements within the location. Data sources can include:
- Aerial Photographs and Satellite Imagery: These provide a bird’s-eye view of the location, aiding in identifying features and landmarks.
- Maps and Plans: Existing maps, site plans, and blueprints offer valuable information on the location’s layout and infrastructure.
- Surveys and Field Observations: Direct observation and surveys can provide detailed information about specific features and their characteristics.
- Data Processing and Organization: Once collected, data needs to be processed and organized for mapping. This may involve converting data formats, cleaning inconsistencies, and establishing a consistent coordinate system.
2. Map Design and Layout:
- Choosing a Map Projection: The choice of map projection significantly impacts the map’s accuracy and appearance. Different projections distort the Earth’s surface in unique ways, so selecting the most appropriate one is crucial.
- Determining the Map Scale: The map scale defines the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances in the real world. Choosing the appropriate scale is essential for ensuring clarity and readability.
- Selecting Map Symbols and Legends: Consistent and clear symbols are used to represent various features on the map. A legend provides a key to understanding these symbols and their meanings.
- Designing the Layout: The map’s layout should be visually appealing and easy to navigate. This involves arranging elements strategically, considering factors like visual hierarchy, contrast, and color schemes.
3. Map Creation and Production:
- Utilizing Mapping Software: Specialized mapping software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, or Google Maps, offers powerful tools for creating maps. These programs allow users to import data, manipulate layers, customize symbols, and generate maps in various formats.
- Manual Map Creation: While less common today, manual map creation using drafting tools and traditional techniques is still relevant for certain applications.
- Map Printing and Distribution: Once the map is complete, it needs to be printed or distributed digitally. The format and distribution method depend on the intended audience and purpose.
Types of Location Maps
Location maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and purposes. Here are some common types:
- Road Maps: These maps depict road networks, highways, and other transportation routes, offering a comprehensive overview of the road infrastructure within a region.
- Topographical Maps: These maps represent the Earth’s surface, including elevation contours, terrain features, and water bodies. They are often used for hiking, camping, and outdoor activities.
- City Maps: These maps focus on urban areas, showcasing streets, buildings, parks, and other points of interest. They are commonly used by tourists and residents for navigation and exploration.
- Floor Plans: These maps depict the layout of individual buildings, showing rooms, hallways, and other internal features. They are essential for navigating within a building, understanding its layout, and locating specific spaces.
- Site Plans: These maps illustrate the layout of a specific site, such as a construction project, a park, or a commercial property. They depict buildings, structures, landscaping, and other relevant features.
- Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific data or themes, such as population density, crime rates, or environmental factors. They use visual representations to communicate information and facilitate analysis.
Benefits of Creating Location Maps
The creation of location maps offers a range of benefits, enhancing communication, facilitating decision-making, and promoting understanding:
- Improved Communication: Location maps provide a clear and concise way to convey information about a specific location, reducing ambiguity and promoting understanding.
- Enhanced Navigation: They guide users through unfamiliar environments, reducing confusion and enabling efficient navigation.
- Data Visualization: Maps offer a visual representation of data, enabling analysis, identification of patterns, and informed decision-making.
- Planning and Development: Location maps facilitate planning and development projects by visualizing designs, communicating ideas, and fostering collaboration.
- Education and Research: They serve as valuable resources for learning and research, providing visual representations of historical events, geographical features, or scientific data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Location Maps
Q: What software is best for creating location maps?
A: Various software options are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Popular choices include:
- ArcGIS: A professional-grade mapping software known for its advanced capabilities and suitability for complex projects.
- QGIS: A free and open-source alternative to ArcGIS, offering a user-friendly interface and powerful features.
- Google Maps: A readily accessible online mapping tool with a wide range of features, including map creation, data visualization, and sharing capabilities.
- Other specialized software: Depending on the specific requirements, other software options may be suitable, such as AutoCAD for architectural drawings or specialized GIS software for specific applications.
Q: How do I choose the right map projection for my location map?
A: The choice of map projection depends on the location’s size, shape, and the intended purpose of the map.
- Conic Projections: Suitable for regions with a north-south orientation, minimizing distortion along meridians.
- Cylindrical Projections: Suitable for mapping the entire globe, minimizing distortion along the equator.
- Azimuthal Projections: Suitable for mapping polar regions, minimizing distortion around the poles.
Q: What are some tips for creating a user-friendly location map?
A: Here are some key tips for ensuring user-friendliness:
- Clear and Concise Symbols: Use easily recognizable and consistent symbols to represent features on the map.
- Comprehensive Legend: Provide a detailed legend that explains the meaning of all symbols used on the map.
- Visual Hierarchy: Emphasize important features through size, color, or other visual cues to guide the user’s attention.
- Intuitive Layout: Arrange map elements logically, considering visual flow and user experience.
- Appropriate Scale: Choose a scale that provides sufficient detail without overwhelming the user.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of my location map?
A: Accuracy is paramount for any location map. Here are some steps to ensure accuracy:
- Reliable Data Sources: Utilize reputable and up-to-date data sources for information on the location.
- Verification and Validation: Double-check data for inconsistencies and errors before incorporating it into the map.
- Ground Truthing: Conduct field observations to verify the accuracy of data and ensure it aligns with real-world conditions.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Communication
Location maps are essential tools for navigating, communicating, and understanding the world around us. They serve as powerful visual representations of physical spaces, facilitating information dissemination, planning, and decision-making. By mastering the art of creating location maps, individuals and organizations can effectively communicate information, promote understanding, and navigate the world with greater clarity and efficiency.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Location Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply