Navigating The World Of Cedars: A Comprehensive Guide To Cedar Tree Identification
Navigating the World of Cedars: A Comprehensive Guide to Cedar Tree Identification
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Cedars: A Comprehensive Guide to Cedar Tree Identification
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Cedars: A Comprehensive Guide to Cedar Tree Identification. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Cedars: A Comprehensive Guide to Cedar Tree Identification

The world of trees is vast and diverse, with countless species offering unique characteristics and ecological roles. Among these, cedar trees stand out with their majestic stature, fragrant wood, and historical significance. However, identifying cedar trees can be challenging due to the numerous species and their wide geographical distribution. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear and informative understanding of cedar trees, focusing on their identification, characteristics, and cultural importance.
Understanding the Cedar Family:
The term "cedar" is often used loosely, encompassing various species that belong to different genera and families. This can lead to confusion, especially when distinguishing true cedars from other coniferous trees. To ensure accurate identification, it is crucial to understand the taxonomic classification of cedar trees.
True Cedars (Cedrus):
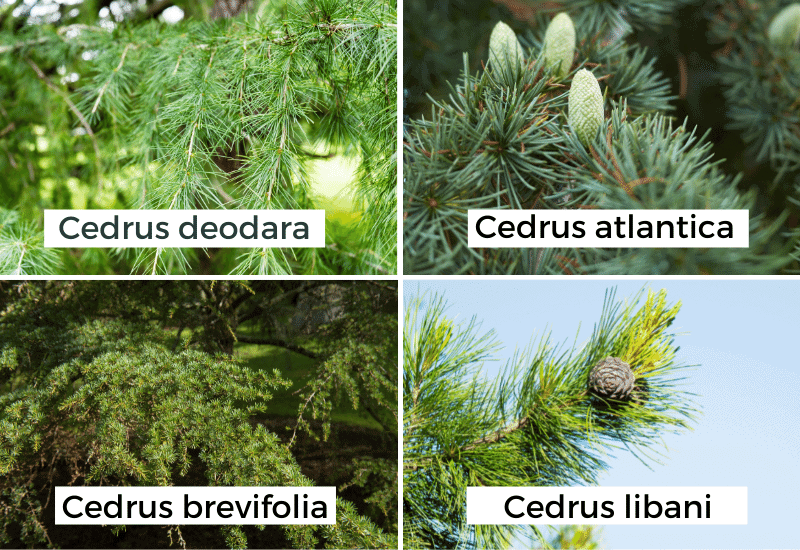
True cedars belong to the genus Cedrus, which comprises four species:
- Atlas Cedar (Cedrus atlantica): Native to the Atlas Mountains of Morocco and Algeria, this species is characterized by its bluish-green needles and spreading branches.
- Cedar of Lebanon (Cedrus libani): Found in the mountainous regions of Lebanon, Syria, and Turkey, this species is renowned for its horizontal branches and dense foliage.
- Cyprus Cedar (Cedrus brevifolia): Endemic to the Troodos Mountains of Cyprus, this species is smaller than other cedars and features dark green needles.
- Deodar Cedar (Cedrus deodara): Originating in the western Himalayas, this species is known for its drooping branches and pendulous foliage.
False Cedars:
Several other coniferous trees are commonly referred to as "cedars" despite not belonging to the Cedrus genus. These include:
- Eastern Red Cedar (Juniperus virginiana): This species belongs to the Juniperus genus and is native to eastern North America. It is often confused with true cedars due to its aromatic wood and similar appearance.
- Western Red Cedar (Thuja plicata): This species belongs to the Thuja genus and is native to the Pacific Northwest of North America. Its distinctive reddish-brown bark and flat, scale-like leaves differentiate it from true cedars.
- Incense Cedar (Calocedrus decurrens): This species belongs to the Calocedrus genus and is native to western North America. It is characterized by its distinctive, aromatic foliage and cone shape.
Key Identification Features:
Distinguishing true cedars from false cedars requires careful observation of specific features:
- Needles: True cedars have sharp, pointed needles that are arranged in clusters, while false cedars have scale-like or flattened needles.
- Cones: True cedar cones are large and barrel-shaped, while false cedar cones are smaller and often have a more rounded or elongated shape.
- Bark: True cedar bark is typically rough and fissured, while false cedar bark can be smooth or scaly.
- Growth Habit: True cedars have a distinctive pyramidal or spreading growth habit, while false cedars can be more upright or shrubby.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
Cedars have played a significant role in human history and culture:
- Religious Symbolism: In various cultures, cedar trees hold religious significance, representing strength, longevity, and divine protection.
- Architectural and Construction Uses: Cedar wood is prized for its durability, fragrance, and resistance to decay, making it a valuable material for construction, furniture, and shipbuilding.
- Medicinal Properties: Cedar oil and extracts have been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat various ailments, including respiratory problems, skin infections, and muscle aches.
Benefits of Cedar Trees:
Beyond their cultural significance, cedar trees offer numerous ecological benefits:
- Habitat Provision: Cedar trees provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife, including birds, squirrels, and insects.
- Soil Stabilization: Cedar trees help prevent soil erosion and improve soil quality.
- Air Purification: Cedar trees absorb pollutants from the air, improving air quality and reducing the risk of respiratory problems.
FAQs about Cedar Trees:
Q: How long do cedar trees live?
A: Cedar trees are long-lived, with some species reaching ages of over 1,000 years.
Q: Are cedar trees poisonous?
A: While cedar trees are not considered poisonous, some people may experience allergic reactions to their pollen or sap.
Q: Can I grow a cedar tree in my garden?
A: Yes, cedar trees can be grown in gardens, but it is important to choose a species that is suitable for your climate and soil conditions.
Q: How do I care for a cedar tree?
A: Cedar trees require well-drained soil and full sun to thrive. They are relatively low-maintenance trees, but regular watering and fertilization are recommended.
Q: What are some common cedar tree diseases?
A: Cedar trees are susceptible to various diseases, including cedar-apple rust, root rot, and canker.
Tips for Identifying Cedar Trees:
- Observe the needles: Pay close attention to the shape, size, and arrangement of the needles.
- Examine the cones: Note the size, shape, and color of the cones.
- Inspect the bark: Observe the texture, color, and patterns of the bark.
- Consider the growth habit: Pay attention to the overall shape and form of the tree.
- Consult a field guide or online resource: Use reliable sources to confirm your identification.
Conclusion:
Cedar trees are majestic and enduring symbols of nature’s resilience and beauty. Recognizing and appreciating the diverse species of cedars requires careful observation and understanding of their unique characteristics. By gaining a deeper understanding of these remarkable trees, we can better appreciate their cultural significance, ecological benefits, and the role they play in shaping our world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Cedars: A Comprehensive Guide to Cedar Tree Identification. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply