The Concept Of "Greater Germany" And Its Historical Significance
The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance
Related Articles: The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance
- 4 The "Greater Germany" Map: A Visual Representation of a Contested Concept
- 5 Understanding the "Greater Germany" Map: A Guide to Interpretation
- 6 Frequently Asked Questions about the "Greater Germany" Map
- 7 Tips for Understanding and Analyzing the "Greater Germany" Map
- 8 Conclusion: The "Greater Germany" Map and the Dangers of Unchecked Nationalism
- 9 Closure
The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance

The term "Greater Germany" refers to a concept that emerged in the 19th century, advocating for a unified German state encompassing territories beyond the borders of the German Confederation. This concept, deeply intertwined with German nationalism, sought to unite all German-speaking peoples under a single banner, regardless of existing political boundaries.
Historical Context and Ideological Roots
The idea of a "Greater Germany" was rooted in the Romantic nationalism of the 19th century, which emphasized shared language, culture, and history as unifying factors. This movement, spurred by the writings of German intellectuals like Johann Gottfried Herder and Friedrich List, envisioned a united Germany as a powerful and influential nation on the European stage.
The Rise of German Nationalism:
The rise of German nationalism in the 19th century was fueled by several factors:
- Political Fragmentation: Germany was divided into numerous independent states, hindering its economic and political development.
- Economic Growth: The Industrial Revolution saw Germany’s economy booming, fueling aspirations for greater political influence and unity.
- Nationalist Sentiment: The Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815) ignited a sense of national pride and desire for unification among German-speaking populations.
The Concept of "Greater Germany" and its Territorial Ambitions:
The concept of "Greater Germany" encompassed various territories beyond the existing German states, primarily:
- Austria: The Austrian Empire, with its predominantly German-speaking population, was a key target for inclusion in a Greater Germany.
- Sudetenland: This region in Czechoslovakia, with a significant German population, was also considered part of the envisioned Greater Germany.
- Alsace-Lorraine: This region, annexed by France in 1871, was claimed by Germany based on its historical ties and predominantly German-speaking population.
The Impact of "Greater Germany" on European Politics:
The concept of "Greater Germany" had a profound impact on European politics, contributing to:
- The Unification of Germany: The concept served as a driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 under Prussian leadership.
- The Rise of German Imperialism: The pursuit of a Greater Germany fueled Germany’s expansionist policies in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
- The First World War: The desire for territorial expansion and the pursuit of a Greater Germany ultimately contributed to the outbreak of World War I.
The Legacy of "Greater Germany":
The legacy of "Greater Germany" remains a complex and controversial topic. It is associated with both the achievements of a unified Germany and the horrors of its expansionist policies, culminating in the Nazi regime and the atrocities of World War II.
The Concept of "Greater Germany" in the Modern Context:
The concept of "Greater Germany" is no longer a politically viable proposition. The rise of European integration, the fall of the Iron Curtain, and the establishment of independent nations have rendered the idea of a united German state encompassing territories beyond its current borders obsolete. However, the historical legacy of "Greater Germany" continues to shape contemporary debates about national identity, territorial claims, and the dangers of unchecked nationalism.
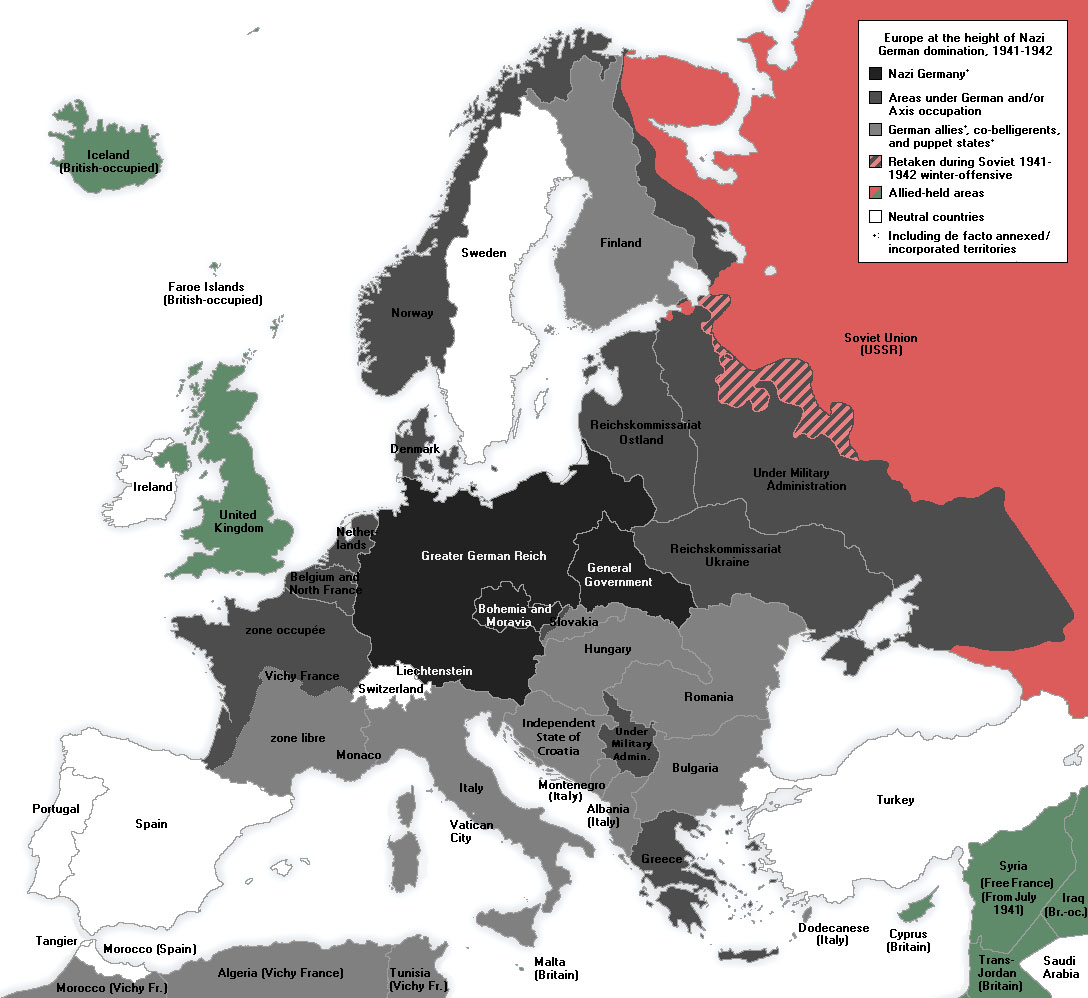
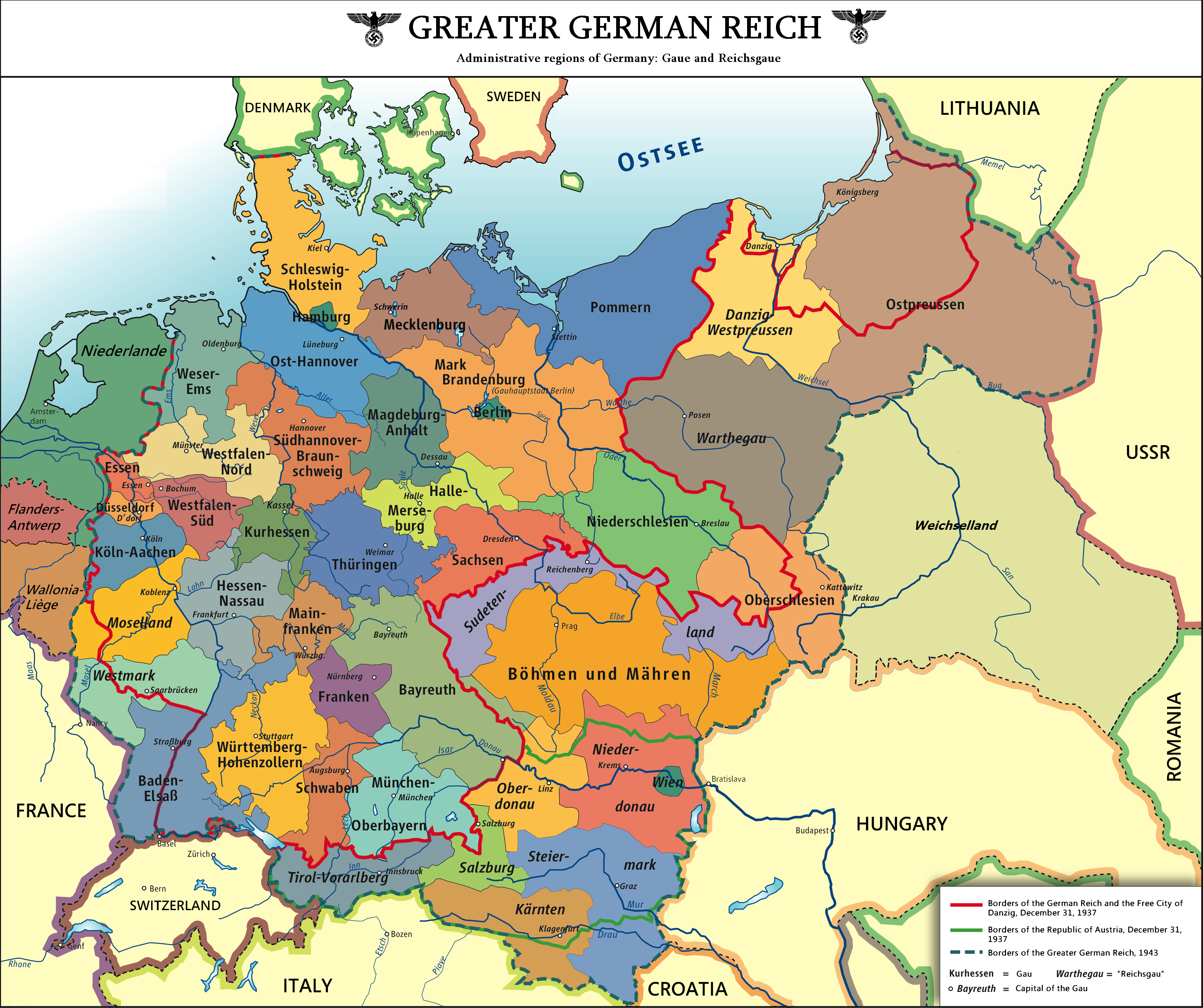
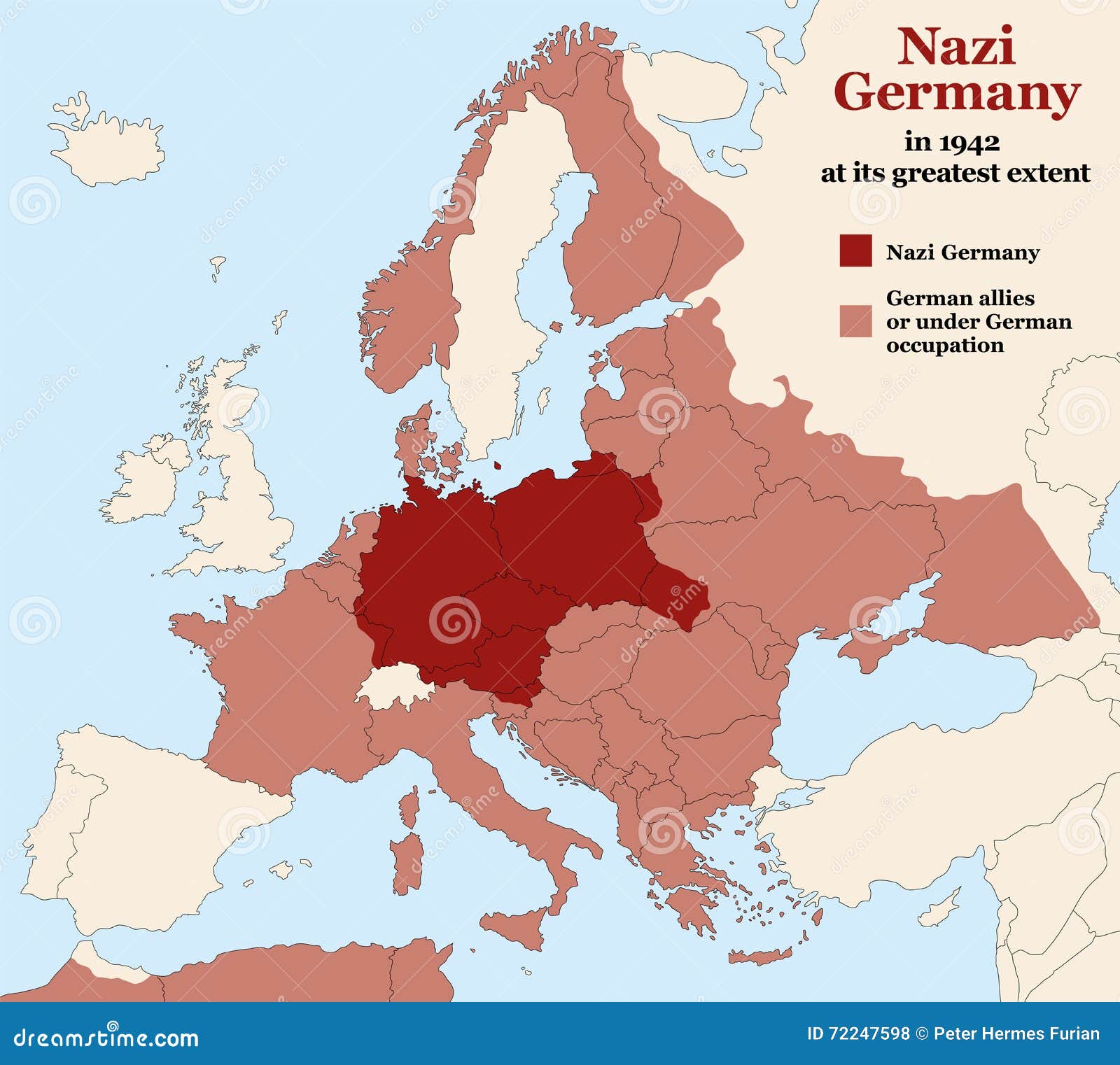
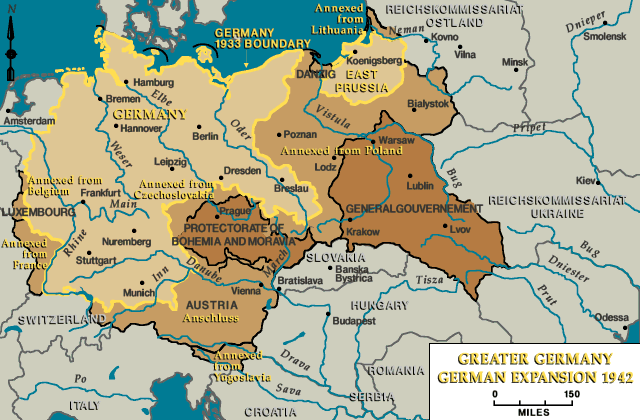
The "Greater Germany" Map: A Visual Representation of a Contested Concept
The "Greater Germany" map, a visual representation of the territorial aspirations associated with this concept, has been subject to various interpretations and controversies throughout history. It is crucial to approach this map with a critical and historical lens, understanding its context and the ideologies it embodies.
The Evolution of the "Greater Germany" Map:
The "Greater Germany" map, as a concept, has undergone various transformations over time, reflecting the evolving ambitions and ideologies associated with German nationalism.
- Early 19th Century: Early maps depicting a "Greater Germany" often focused on uniting the German Confederation and incorporating Austria into a single state.
- Late 19th Century: As German nationalism intensified, maps began to include territories like Alsace-Lorraine and parts of Denmark, reflecting the growing ambition for a larger and more powerful Germany.
- Early 20th Century: During the Nazi era, maps depicting a "Greater Germany" expanded further, incorporating territories like Czechoslovakia, Poland, and parts of the Soviet Union, reflecting the aggressive and expansionist policies of the Nazi regime.
The "Greater Germany" Map: A Tool of Propaganda:
The "Greater Germany" map was often used as a tool of propaganda, promoting the idea of a united and powerful Germany, while justifying territorial claims based on historical ties and linguistic similarities. This approach served to legitimize expansionist policies and foster a sense of national unity among the German population.
Interpretations and Controversies:
The "Greater Germany" map has been subject to various interpretations and controversies, highlighting the complexities and dangers associated with the concept:
- Historical Revisionism: Some interpretations of the "Greater Germany" map attempt to downplay or justify the aggressive and expansionist policies associated with it, focusing instead on the historical and linguistic ties between German-speaking populations.
- Nationalist Sentiment: The "Greater Germany" map continues to resonate with some nationalist sentiments, particularly in Germany and Austria, where it is seen as a symbol of national unity and historical grandeur.
- Historical Accuracy: The "Greater Germany" map is often criticized for its lack of historical accuracy and for promoting a distorted view of the past, ignoring the diverse ethnic and cultural realities of the regions it encompasses.
The "Greater Germany" Map: A Reminder of the Dangers of Nationalism:
The "Greater Germany" map serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism and the potential for it to lead to aggression, expansionism, and violence. It underscores the importance of critical thinking, historical accuracy, and the recognition of diverse cultural and ethnic identities in understanding the complexities of historical narratives.
Understanding the "Greater Germany" Map: A Guide to Interpretation
To understand the "Greater Germany" map and its significance, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
- Historical Context: The map must be viewed within the context of the historical events and ideologies that shaped its creation.
- Political Ambitions: The map reflects the political ambitions and territorial aspirations of different groups and movements at different points in history.
- Ideological Underpinnings: The map is deeply intertwined with the ideologies of German nationalism, which emphasized language, culture, and history as unifying factors.
- Ethnic and Cultural Diversity: The map often ignores the diverse ethnic and cultural realities of the regions it encompasses, simplifying complex historical narratives.
- Consequences of Expansionism: The map highlights the consequences of expansionist policies, which often lead to conflict, violence, and the displacement of populations.
The "Greater Germany" Map: A Tool for Critical Analysis:
The "Greater Germany" map should not be seen as a definitive or objective representation of historical reality. Instead, it should be used as a tool for critical analysis, prompting questions about the nature of national identity, the limits of territorial claims, and the dangers of unchecked nationalism.
Frequently Asked Questions about the "Greater Germany" Map
1. What is the "Greater Germany" map?
The "Greater Germany" map is a visual representation of the territorial aspirations associated with the concept of a unified German state encompassing territories beyond the borders of the German Confederation.
2. What territories were included in the "Greater Germany" map?
The "Greater Germany" map included various territories beyond the existing German states, primarily Austria, Sudetenland, and Alsace-Lorraine.
3. What was the historical context of the "Greater Germany" map?
The "Greater Germany" map emerged during the 19th century, fueled by German nationalism and the desire for a unified and powerful German state.
4. What were the ideological underpinnings of the "Greater Germany" map?
The "Greater Germany" map was deeply intertwined with the ideologies of German nationalism, which emphasized language, culture, and history as unifying factors.
5. What were the consequences of the "Greater Germany" concept?
The "Greater Germany" concept contributed to the unification of Germany in 1871, fueled German imperialism, and ultimately contributed to the outbreak of World War I.
6. Is the "Greater Germany" map a reliable historical document?
The "Greater Germany" map should be viewed with caution and interpreted within its historical context. It reflects the political ambitions and ideologies of the time, but it is not a neutral or objective representation of historical reality.
7. What are the dangers of using the "Greater Germany" map as a source of historical information?
Using the "Greater Germany" map as a source of historical information can lead to misinterpretations, historical revisionism, and the promotion of nationalist ideologies.
8. What is the legacy of the "Greater Germany" map?
The legacy of the "Greater Germany" map is complex and controversial. It is associated with both the achievements of a unified Germany and the horrors of its expansionist policies, culminating in the Nazi regime and the atrocities of World War II.
9. Is the "Greater Germany" concept relevant in the modern context?
The concept of "Greater Germany" is no longer a politically viable proposition. However, its historical legacy continues to shape contemporary debates about national identity, territorial claims, and the dangers of unchecked nationalism.
10. How should the "Greater Germany" map be interpreted?
The "Greater Germany" map should be interpreted with a critical and historical lens, understanding its context, the ideologies it embodies, and the consequences of the territorial aspirations it represents.
Tips for Understanding and Analyzing the "Greater Germany" Map
- Focus on Historical Context: Always consider the historical events and ideologies that shaped the creation of the map.
- Examine Political Ambitions: Analyze the political ambitions and territorial aspirations reflected in the map.
- Understand Ideological Underpinnings: Recognize the ideologies of nationalism and expansionism that underpin the map.
- Acknowledge Ethnic and Cultural Diversity: Consider the diverse ethnic and cultural realities of the regions encompassed by the map.
- Explore Consequences of Expansionism: Investigate the consequences of expansionist policies, including conflict, violence, and displacement of populations.
Conclusion: The "Greater Germany" Map and the Dangers of Unchecked Nationalism
The "Greater Germany" map, a visual representation of a contested concept, serves as a reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism and the potential for it to lead to aggression, expansionism, and violence. It underscores the importance of critical thinking, historical accuracy, and the recognition of diverse cultural and ethnic identities in understanding the complexities of historical narratives.
By approaching the "Greater Germany" map with a critical and historical lens, we can gain a deeper understanding of the historical context that shaped its creation, the ideologies it embodies, and the consequences of the territorial aspirations it represents. This understanding is crucial for preventing the resurgence of nationalist ideologies and ensuring a more peaceful and inclusive future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Concept of "Greater Germany" and Its Historical Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply