The Power Of Interactive Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Annotation And Collaboration
The Power of Interactive Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Annotation and Collaboration
Related Articles: The Power of Interactive Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Annotation and Collaboration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Interactive Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Annotation and Collaboration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Interactive Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Annotation and Collaboration

In an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to visualize and interact with information is paramount. Maps, long serving as powerful tools for navigation and understanding spatial relationships, have evolved to become dynamic platforms for communication, collaboration, and knowledge creation. The emergence of interactive maps, those that allow users to annotate, highlight, and share insights directly on the map interface, has revolutionized the way we engage with geographical data. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse applications, benefits, and functionalities of interactive maps, demonstrating their transformative potential across various fields.
Understanding Interactive Maps: Beyond Static Representations
Traditional maps, while valuable for conveying basic spatial information, often lack the flexibility and interactivity required for modern-day tasks. Interactive maps bridge this gap by offering users the ability to engage with maps in a more dynamic and personalized way. Key features that define interactive maps include:
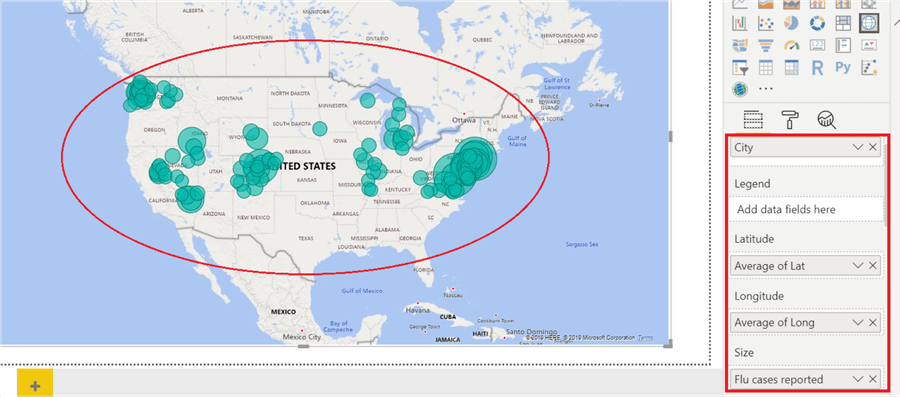
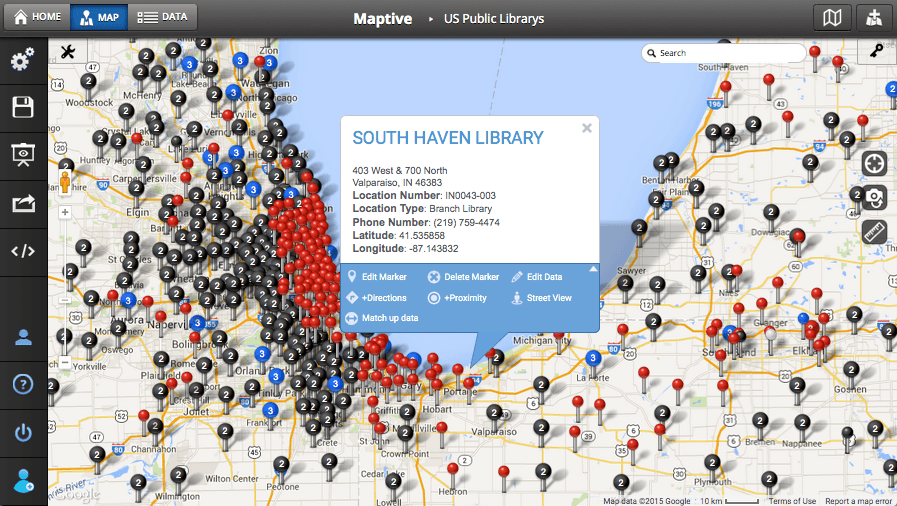
- Annotation: Users can add notes, markers, lines, shapes, and other annotations directly onto the map, highlighting specific areas of interest, adding contextual information, or marking points of significance.
- Collaboration: Interactive maps facilitate real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to contribute annotations, share insights, and work together on a single map.
- Customization: Users can personalize the map by adjusting its layers, adding custom data, and tailoring the visual representation to suit their specific needs.
- Data Integration: Interactive maps can seamlessly integrate with other data sources, enabling users to visualize and analyze spatial data alongside other relevant information.
Applications: Unlocking the Potential of Interactive Maps
The versatility of interactive maps extends across a wide range of disciplines, making them indispensable tools for various tasks:
- Education: Interactive maps enhance learning experiences by allowing students to explore geographical concepts, visualize historical events, and engage in collaborative projects.
- Urban Planning: City planners leverage interactive maps to analyze urban development, identify potential areas for infrastructure improvements, and assess the impact of proposed projects.
- Environmental Management: Environmental agencies utilize interactive maps to track environmental changes, monitor natural resources, and manage conservation efforts.
- Business and Marketing: Businesses utilize interactive maps for market research, identifying target demographics, optimizing logistics, and visualizing sales data.
- Disaster Response: Interactive maps play a critical role in emergency response by providing real-time information on disaster areas, evacuation routes, and resource allocation.
- Healthcare: Interactive maps aid in disease tracking, resource distribution, and identifying healthcare access disparities.
- Research and Development: Researchers employ interactive maps for data visualization, spatial analysis, and collaborative research projects.
Benefits: Empowering Collaboration and Insight
The use of interactive maps brings numerous benefits, significantly enhancing efficiency, communication, and decision-making:
- Enhanced Visual Communication: Interactive maps provide a clear and intuitive way to communicate complex spatial information, making it easier for individuals to understand and interpret data.
- Improved Collaboration: Interactive maps foster collaboration by allowing multiple users to work on the same map simultaneously, share insights, and contribute to a collective understanding of the data.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Interactive maps enable data-driven decision making by providing users with the tools to analyze spatial data, identify patterns, and draw informed conclusions.
- Increased Efficiency: Interactive maps streamline workflows by providing a centralized platform for data visualization, annotation, and collaboration, reducing the need for multiple tools and communication channels.
- Enhanced Engagement: Interactive maps engage users through their dynamic and interactive nature, fostering a more immersive and engaging experience.
Key Features and Functionalities
Interactive maps come equipped with a range of features and functionalities that empower users to effectively utilize them:
- Base Maps: Users can choose from various base maps, including satellite imagery, topographic maps, and street maps, to provide context and visual reference.
- Layers: Interactive maps allow users to add and manage layers, such as points of interest, demographic data, or environmental information, to visualize different datasets on the same map.
- Markers and Symbols: Users can add markers and symbols to the map to highlight specific locations, indicate different categories of data, or represent specific events.
- Lines and Shapes: Interactive maps enable users to draw lines and shapes on the map to represent boundaries, routes, or other spatial relationships.
- Annotations: Users can add text annotations, including notes, labels, and descriptions, to provide additional information and context to the map.
- Measurement Tools: Interactive maps often include tools for measuring distances, areas, and other spatial parameters.
- Search Functionality: Users can search for specific locations, points of interest, or addresses within the map.
- Data Integration: Interactive maps allow users to integrate data from external sources, such as spreadsheets, databases, or APIs, to enrich the map with additional information.
- Sharing and Collaboration: Interactive maps facilitate sharing and collaboration by allowing users to export maps, share links, and collaborate on the same map in real-time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are some popular interactive map platforms?
Several popular platforms offer interactive mapping capabilities, including Google Maps, ArcGIS Online, Mapbox, Leaflet, and OpenLayers.
2. How can I create my own interactive map?
There are various ways to create interactive maps:
- Online Mapping Platforms: Platforms like Google My Maps, ArcGIS Online, and Mapbox provide user-friendly interfaces for creating maps without coding experience.
- Mapping Libraries: Developers can use mapping libraries like Leaflet and OpenLayers to create custom interactive maps with more flexibility and control.
3. What are some best practices for using interactive maps effectively?
- Choose the Right Platform: Select a platform that meets your specific needs and functionalities.
- Clear and Concise Annotations: Use clear and concise language for annotations to avoid confusion.
- Use Visual Hierarchy: Utilize different marker colors, sizes, and symbols to create visual hierarchy and emphasize important information.
- Maintain Data Accuracy: Ensure the data used in the map is accurate and up-to-date.
- Share Effectively: Choose appropriate sharing methods to ensure the map reaches the intended audience.
Tips for Using Interactive Maps Effectively
- Start with a clear purpose: Define the goal of your map before you begin.
- Choose the right data: Select data relevant to your purpose and audience.
- Use clear and concise annotations: Make your annotations easy to understand and read.
- Employ visual hierarchy: Use color, size, and shape to highlight key information.
- Integrate with other tools: Combine interactive maps with other tools for data analysis and visualization.
- Share and collaborate: Share your maps with others to foster collaboration and communication.
Conclusion
Interactive maps have become essential tools for visualizing, analyzing, and communicating spatial information in today’s data-driven world. Their ability to empower users with annotation, collaboration, and customization capabilities makes them invaluable across various fields. By harnessing the power of interactive maps, individuals and organizations can unlock new insights, facilitate collaboration, and make informed decisions based on spatial data. As technology continues to evolve, interactive maps will continue to play an increasingly vital role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving innovation across diverse sectors.




![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Interactive Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Annotation and Collaboration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply