Understanding The Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Network Infrastructure Optimization
Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization
Related Articles: Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization
- 3.1 What is the Lower Com Field Map?
- 3.2 Benefits of Utilizing a Lower Com Field Map
- 3.3 Applications of the Lower Com Field Map
- 3.4 Creating and Maintaining a Lower Com Field Map
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Creating an Effective Lower Com Field Map
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization
The lower com field map, also known as the "lower layer com field map" or simply "lower com map," is a critical component of network infrastructure optimization. It provides a visual representation of the physical and logical connections between network devices, offering valuable insights into the network’s topology and performance. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the lower com field map, exploring its purpose, benefits, and applications in modern network management.
What is the Lower Com Field Map?
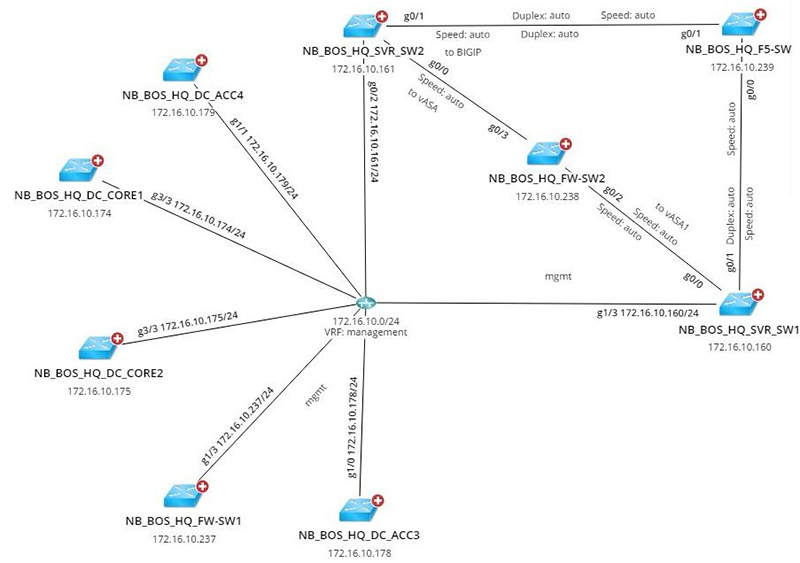
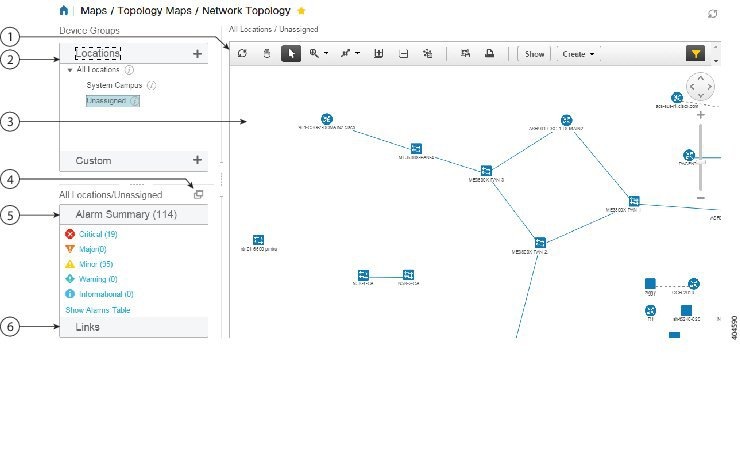
The lower com field map is a graphical representation of the lower layers of the OSI model, specifically layers 1 and 2: the physical and data link layers. It depicts the physical connections between network devices, such as switches, routers, servers, and workstations, along with the associated cabling and other physical infrastructure.
Key Elements of a Lower Com Field Map:
- Devices: Each network device, including switches, routers, servers, and workstations, is represented by a unique symbol.
- Connections: Lines connecting devices represent the physical links between them, indicating the type of cabling used (e.g., copper, fiber optic) and the specific port connections.
- Network Segments: The map can be divided into segments, representing different network zones or subnets, highlighting the flow of data within the network.
- Labels: Each device and connection is labeled with relevant information, such as device names, IP addresses, port numbers, and cable types.
Benefits of Utilizing a Lower Com Field Map
The lower com field map offers numerous advantages for network administrators and engineers, significantly aiding in network management, troubleshooting, and planning:
1. Enhanced Network Visibility:
The map provides a clear and concise overview of the network’s physical layout, revealing the connections between devices and the flow of data. This visual representation facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the network’s structure and helps identify potential bottlenecks or points of failure.
2. Simplified Troubleshooting:
By mapping the physical connections, the lower com field map assists in quickly isolating problems within the network. Network administrators can readily identify faulty cables, malfunctioning ports, or device connectivity issues, expediting troubleshooting efforts.
3. Efficient Network Planning:
The map serves as a valuable tool for network planning, aiding in the design and deployment of new infrastructure. It allows administrators to visualize potential changes, assess the impact of new devices or connections, and optimize network performance before implementation.
4. Improved Security:
By understanding the physical connections within the network, administrators can identify potential security vulnerabilities. The map helps in implementing security measures, such as physical access control, cable management, and device isolation, to safeguard sensitive data.
5. Documentation and Communication:
The lower com field map serves as a valuable documentation tool, providing a comprehensive record of the network’s physical infrastructure. It facilitates communication and collaboration between network teams, ensuring a consistent understanding of the network’s layout and configuration.
Applications of the Lower Com Field Map
The lower com field map finds practical applications in various network management scenarios:
1. Network Design and Deployment:
The map is crucial in the initial planning stages of network design, allowing for the visualization of the proposed infrastructure, the selection of appropriate devices and cabling, and the estimation of network capacity.
2. Network Monitoring and Management:
The map aids in ongoing network monitoring and management, allowing for the identification of performance issues, network congestion, and potential security threats. It facilitates proactive maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal network performance.
3. Network Troubleshooting:
The map is an indispensable tool for troubleshooting network problems, enabling the rapid isolation of faulty components, connectivity issues, or configuration errors. It helps identify the root cause of network failures, leading to faster resolution and reduced downtime.
4. Network Security Audits:
The map plays a vital role in network security audits, allowing security professionals to assess the physical security of the network infrastructure, identify potential vulnerabilities, and recommend security enhancements.
5. Disaster Recovery Planning:
The map is essential for disaster recovery planning, providing a detailed record of the network infrastructure, facilitating the restoration of network connectivity in the event of a disaster.
Creating and Maintaining a Lower Com Field Map
Several tools and techniques can be used to create and maintain a lower com field map:
1. Network Management Software:
Dedicated network management software often includes features for automatically generating lower com field maps based on network device data. These tools offer interactive maps, allowing for real-time updates and detailed information about each device and connection.
2. Drawing Software:
General-purpose drawing software, such as Microsoft Visio or Adobe Illustrator, can be used to create custom lower com field maps. This approach provides flexibility in design and allows for the inclusion of specific details tailored to the network’s needs.
3. Network Discovery Tools:
Network discovery tools can scan the network, automatically identifying devices and connections. This data can be used to populate the lower com field map, streamlining the mapping process.
4. Manual Documentation:
In smaller networks or for specific network segments, manual documentation can be employed. This involves manually recording device information, connections, and cabling details, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
5. Regular Updates:
It is essential to regularly update the lower com field map to reflect changes in the network infrastructure, such as new device installations, cable replacements, or network configuration updates. This ensures the map remains an accurate representation of the network’s current state.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between a lower com field map and a logical network diagram?
A lower com field map focuses on the physical connections between devices, depicting the network’s physical infrastructure. In contrast, a logical network diagram represents the logical connections between devices, showing the flow of data and network services.
2. What is the best way to create a lower com field map?
The best approach depends on the size and complexity of the network. Network management software offers automated mapping capabilities, while drawing software provides flexibility for customization. For smaller networks, manual documentation can be sufficient.
3. How often should I update my lower com field map?
Regular updates are crucial to ensure the map remains accurate. Ideally, the map should be updated whenever there are significant changes to the network infrastructure, such as new device installations, cable replacements, or network configuration updates.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a lower com field map?
Common mistakes include neglecting to update the map regularly, omitting critical details, using inconsistent symbols or labels, and failing to consider the network’s physical layout.
5. Can I use the lower com field map to troubleshoot network problems?
Yes, the map is a valuable tool for troubleshooting network issues. It helps identify faulty cables, malfunctioning ports, or device connectivity problems, facilitating the isolation of the problem area.
Tips for Creating an Effective Lower Com Field Map
- Maintain a clear and concise layout: Use easily understandable symbols and labels, ensuring the map is easy to navigate and interpret.
- Include detailed information: Include device names, IP addresses, port numbers, cable types, and other relevant information to provide comprehensive context.
- Consider the network’s physical layout: Represent the physical placement of devices and connections accurately to reflect the network’s actual configuration.
- Update regularly: Ensure the map is kept up-to-date with any changes to the network infrastructure to maintain its accuracy and relevance.
- Utilize standardized symbols and labels: Employ industry-standard symbols and labels to ensure consistency and clarity across different network diagrams.
Conclusion
The lower com field map is a powerful tool for network administrators and engineers, providing valuable insights into the network’s physical infrastructure. By understanding the connections between devices and the flow of data, the map facilitates network management, troubleshooting, planning, and security. Implementing a comprehensive lower com field map strategy ensures efficient network operations, minimizes downtime, and safeguards sensitive data. Utilizing the right tools and techniques for creating and maintaining the map ensures its accuracy and relevance, maximizing its benefits for network optimization and management.



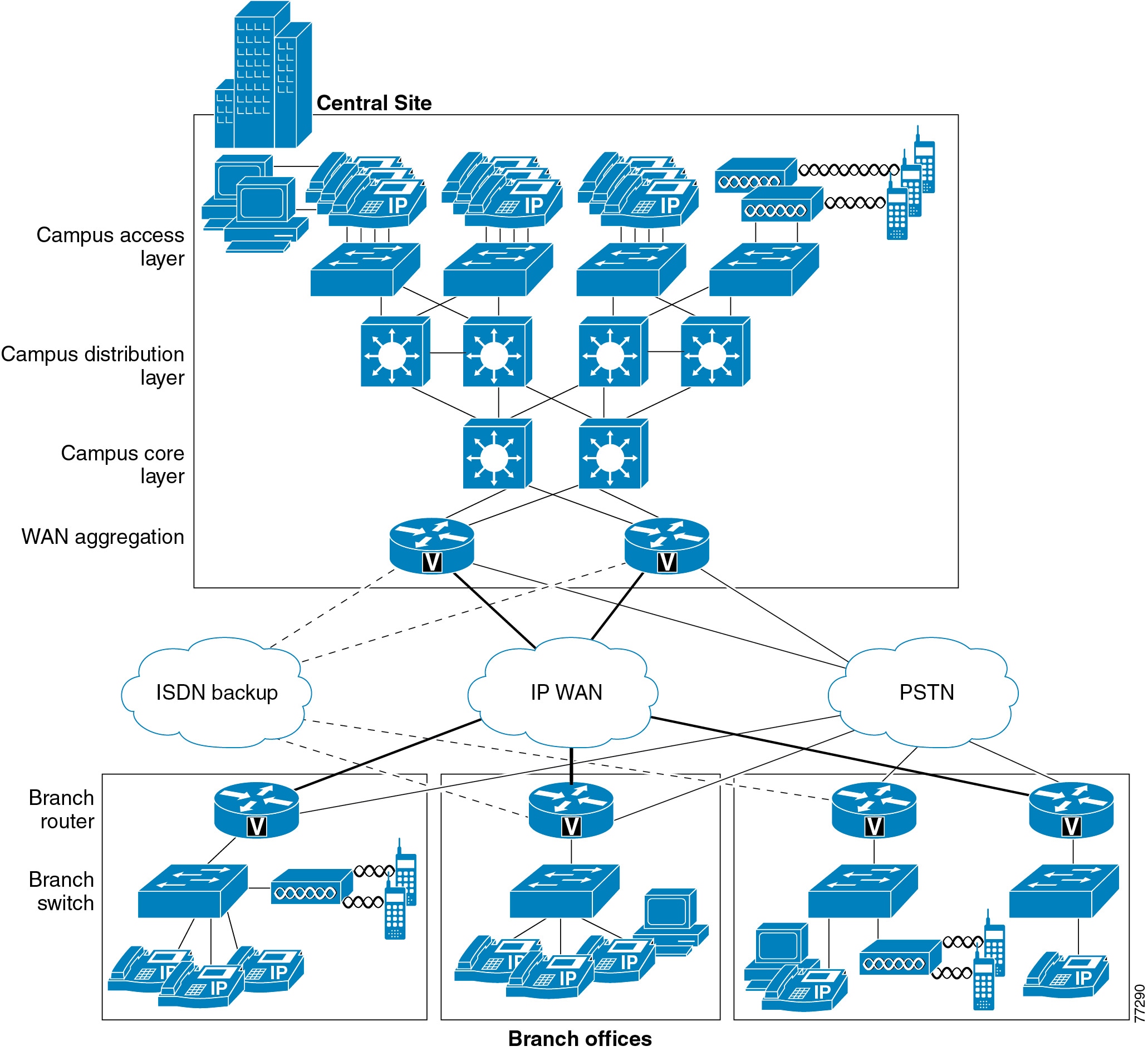
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Lower Com Field Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Infrastructure Optimization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply