Unveiling The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Contour Map Elevation
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Map Elevation
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Map Elevation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Map Elevation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Map Elevation

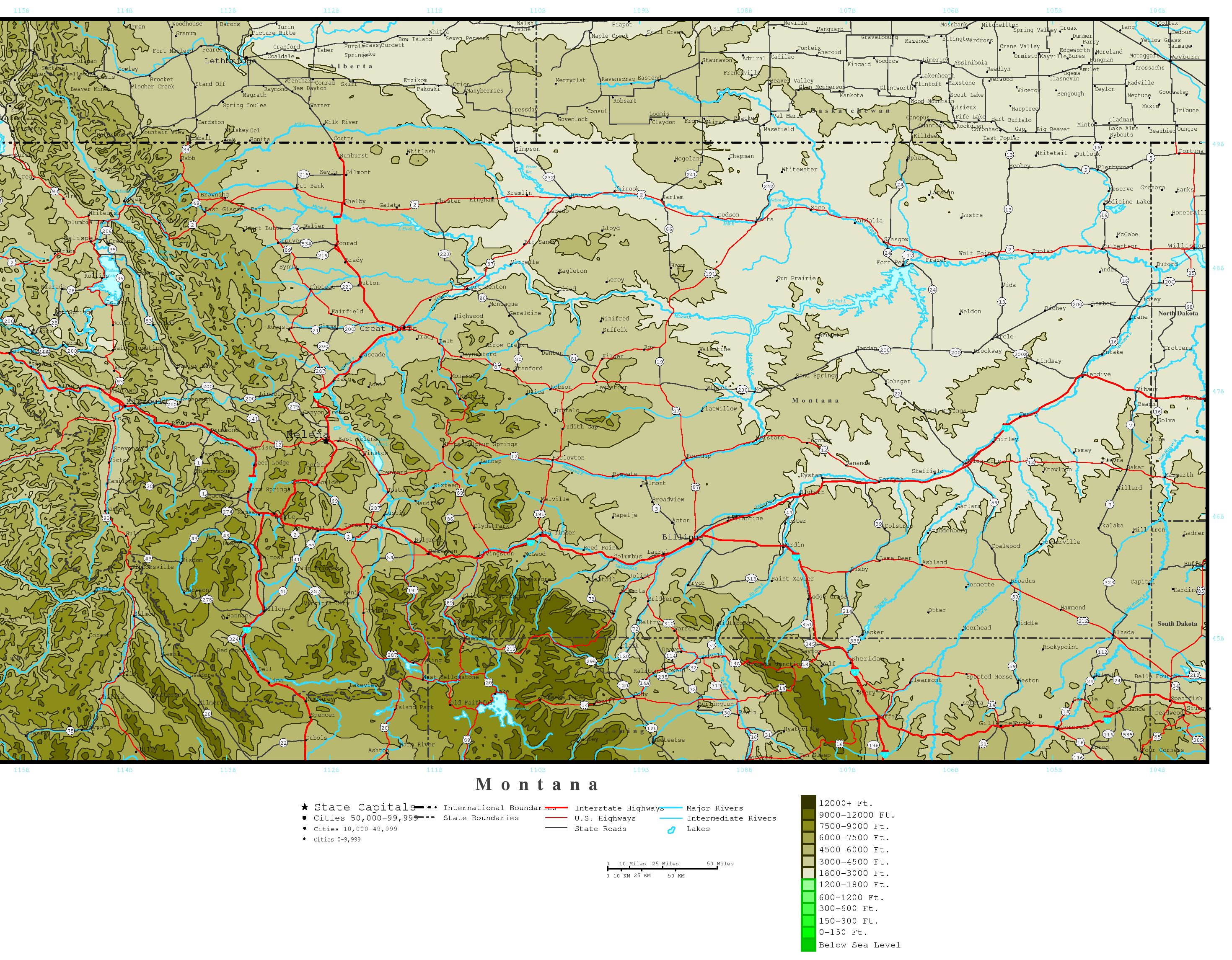
Contour maps are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the topography of an area. They provide a clear and concise representation of the terrain, revealing the elevation of the land at various points through a system of lines known as contours. This article delves into the intricacies of contour map elevation, explaining its significance and applications in various fields.
What is Contour Map Elevation?
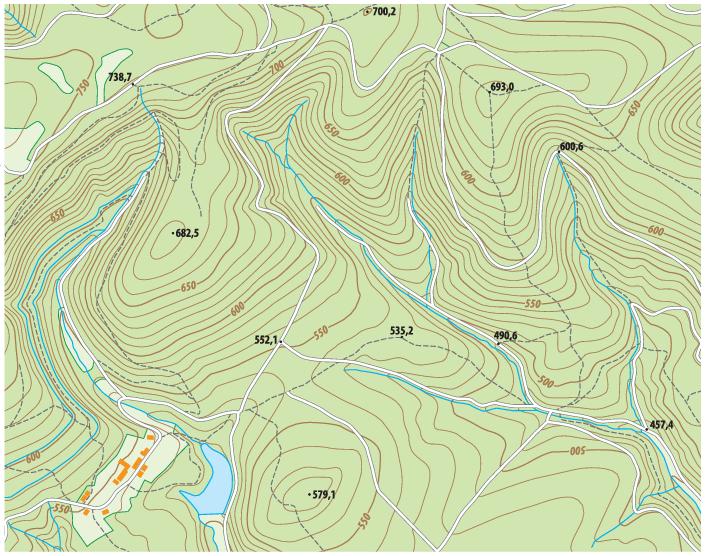
Contour map elevation refers to the height of a specific point on the land surface above a designated datum, typically sea level. These elevations are depicted by contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. Imagine a series of imaginary horizontal slices cutting through a terrain; each slice represents a specific elevation, and the intersection of this slice with the ground surface forms a contour line.
Understanding Contour Lines:
Contour lines hold crucial information about the terrain:
- Elevation: Each contour line represents a specific elevation, typically indicated by a number on the map.
- Slope: The spacing between contour lines reveals the steepness of the terrain. Closely spaced lines indicate a steep slope, while widely spaced lines suggest a gentle incline.
- Landforms: The shape and arrangement of contour lines depict various landforms such as hills, valleys, ridges, and depressions.
Reading Contour Maps:
Interpreting contour maps requires understanding the following key principles:
- Contour lines never cross: This rule ensures that each point on the map has a unique elevation.
- Contour lines follow the terrain: They bend and curve to reflect the shape of the land.
- Closed contour lines represent hills or depressions: A closed loop indicates a summit or a low point.
- Contour lines close at the edge of the map: If a contour line is not closed, it implies that the terrain continues beyond the map’s limits.
Applications of Contour Maps:
Contour maps find wide-ranging applications across various disciplines, including:
- Civil Engineering: Contour maps are vital for planning and constructing infrastructure projects, including roads, bridges, and dams. They enable engineers to assess the feasibility of projects, determine optimal routes, and estimate earthwork volumes.
- Environmental Studies: Contour maps assist in understanding the impact of human activities on the environment, such as deforestation, erosion, and pollution. They help in identifying areas prone to flooding, landslides, and other natural hazards.
- Geology: Geologists use contour maps to map geological formations, identify faults and folds, and understand the distribution of mineral resources.
- Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on contour maps for navigation, planning routes, and assessing the difficulty of trails.
- Agriculture: Contour maps assist farmers in planning irrigation systems, optimizing crop yields, and managing soil erosion.
- Military Operations: Contour maps are essential for planning military campaigns, identifying strategic locations, and navigating complex terrain.
Benefits of Using Contour Maps:
- Visual Representation: Contour maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of the terrain, making it easy to understand the topography of an area.
- Quantitative Data: They offer quantitative data on elevation, slope, and other terrain characteristics, enabling precise analysis and decision-making.
- Multiple Applications: Contour maps are versatile and applicable across diverse fields, making them an invaluable tool for various purposes.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional surveying methods, contour maps provide a cost-effective way to obtain topographic data.
FAQs About Contour Map Elevation:
Q: What is the difference between a contour map and a topographic map?
A: A topographic map is a type of map that includes contour lines, alongside other features such as rivers, roads, and buildings. In essence, a contour map is a specific type of topographic map focusing solely on elevation data.
Q: How are contour maps created?
A: Contour maps are typically created through surveying techniques, using instruments like GPS receivers, total stations, or aerial imagery. These data are then processed and analyzed to generate a digital elevation model (DEM), which is used to create the contour map.
Q: What are the limitations of contour maps?
A: Contour maps represent a simplified representation of the terrain and may not capture all the details of the landscape. They also rely on the accuracy of the survey data used to create them.
Q: How can I learn to read contour maps?
A: There are numerous resources available for learning to read contour maps, including online tutorials, books, and workshops. It is essential to practice interpreting contour lines and understanding their relationship to the terrain.
Tips for Using Contour Maps:
- Study the map legend: The legend provides essential information about the map’s scale, contour interval, and other symbols used.
- Identify key features: Pay attention to prominent landforms such as hills, valleys, and ridges, as they can provide context for navigating the terrain.
- Consider the scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and the accuracy of the elevation data.
- Use a compass and altimeter: These tools can help you navigate the terrain and verify the elevation indicated on the map.
Conclusion:
Contour map elevation is a fundamental concept in understanding and visualizing the topography of an area. These maps provide a wealth of information about the terrain, enabling informed decision-making in various fields. By understanding the principles of contour lines and their applications, individuals can leverage these powerful tools for a wide range of purposes, from planning infrastructure projects to navigating outdoor trails. The ability to interpret contour maps is an invaluable skill for professionals and enthusiasts alike, unlocking the secrets of the landscape and empowering them to navigate, analyze, and understand the world around them.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Map Elevation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Districts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Nangarhar Province Map: Unveiling The Heart Of Eastern Afghanistan
- Navigating The Hub Of The Heartland: A Comprehensive Guide To Kansas City International Airport
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Brooklyn: A Comprehensive Guide To The Borough’s Map
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Linden, Tennessee Map
- Navigating Brussels Airport: A Comprehensive Guide To The Brussels Airport Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Caesar’s Creek: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
- Navigating California’s Natural Wonders: A Comprehensive Guide To State Park Campgrounds
Leave a Reply